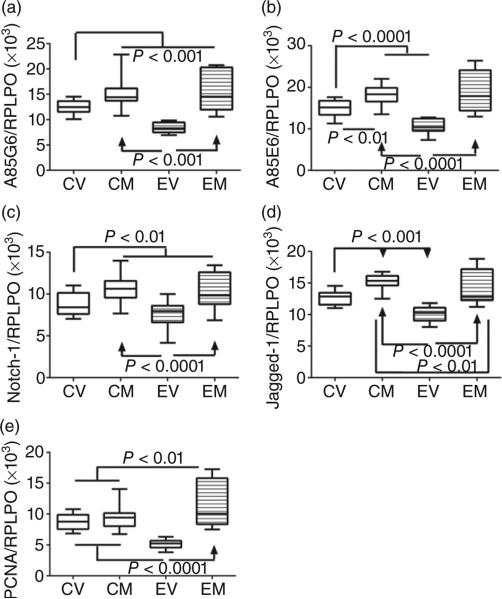
Figure 6.
Effects of chronic ethanol exposure and myriocin treatment on aspartyl-asparaginyl-β-hydroxylase (AAH) and Notch signaling molecules in liver. Livers from control and chronic ethanol-fed rats that were treated with vehicle or myriocin were used to measure (a) AAH-A85G6, (b) AAH/Humbug-A85E6, (c) Notch-1, (d) Jagged-1, and (e) proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunoreactivity by duplex ELISAs. Results were normalized to large ribosomal protein (RPLPO), which was measured in the same wells. Intergroup comparisons were made using calculated protein/RPLPO ratios. CV, control + vehicle; CM, control + myriocin; EV, ethanol + vehicle; EM, ethanol + myriocin; n = 8 or 10 samples per group. Box plots depict medians (horizontal bars), 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower limits of boxes), and ranges (stems). Intergroup comparisons were made by repeated-measures one-way anova with post hoc Tukey tests of significance.