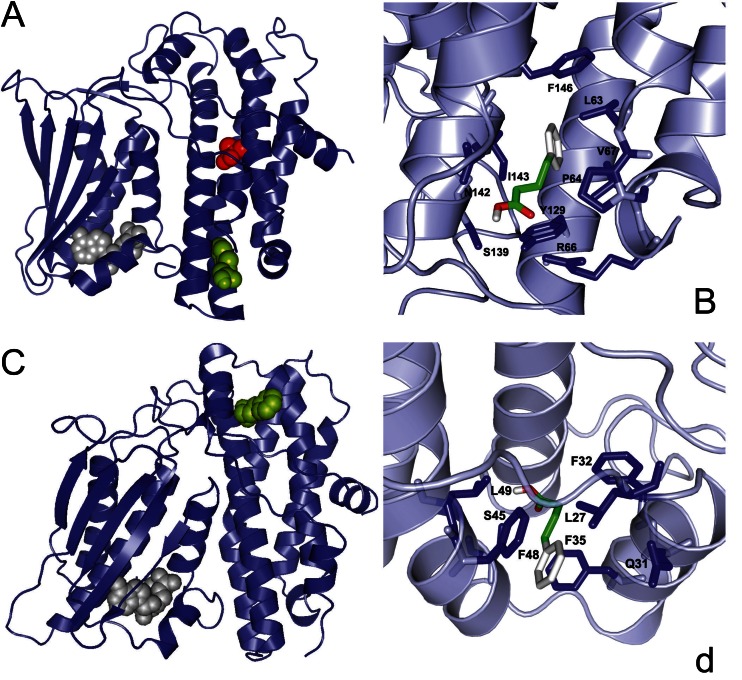
Fig. 4.
Putative binding sites of phenylbutyrate on PDK2 (a, b) and PDK3 (c, d). (a) Ribbon representation of human PDK2 structure (PDB 2BU8) and bound ligands represented in a space-filling model: ATP/Mg2+ in gray; phenylbutyrate in green; DCA in red. ATP and DCA are present in the X-ray structure while the phenylbutyrate position was suggested by docking analysis. (b) Specific interactions of phenylbutyrate (red, green, and white) with amino acid residues (stick representation) at the binding sites of PDK2. (c) Ribbon representation of human PDK3 structure (PDB 2Q8I) and bound ligands represented in a space-filling model: ATP/Mg2+ in gray; phenylbutyrate in green. ATP is present in the X-ray structure while phenylbutyrate binding site was suggested by the docking analysis. (d) Specific interactions of phenylbutyrate with amino acid residues (stick representation) of PDK3 at the binding sites. Van der Waals interaction spheres of the amino acid residues (stick representation) in contact with the inhibitor have been removed for clarity in b and d. Supplementary Fig. 1 shows Van der Waals interaction spheres of the amino acid residues in contact with the inhibitor