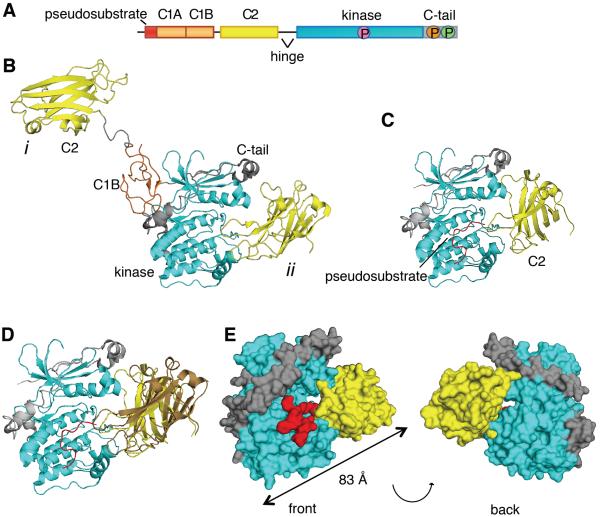
Figure 1. The C2 Domain of PKCβII Interacts with the Kinase Domain and C-Terminal Tail.
(A) Schematic of the primary structure of PKCβII showing domain composition, priming phosphorylation sites (activation loop in pink, turn motif in orange, and hydrophobic motif in green), and the proteolytically-labile hinge that separates the regulatory and catalytic moieties.
(B) Crystal structure of PKCβII (PDBID:3PFQ) showing the original interpretation of the location of the C2 domain that traces polypeptide from the C1B to the C2 (mode i) and the alternative interpretation in which the C2 domain binds the kinase domain by an intramolecular interaction (mode ii). Both modes are present in the crystal packing.
(C) C2 domain (yellow) docked onto a complex of the PKCβII kinase domain (cyan) and the modeled pseudosubstrate (red).
(D) Complex of the PKCβII kinase domain (cyan) and the mode ii C2 domain (yellow) from the crystal packing with the modeled pseudosubstrate (red), superimposed with the docked C2 domain (brown).
(E) Structure of the kinase domain:C2 domain:pseudosubstrate complex showing the opening between the kinase domain (cyan) and the C2 domain (yellow), through which the pseudosubstrate:C1A linker (red) can be accommodated.
See also Figure S2.