Fig. 1.
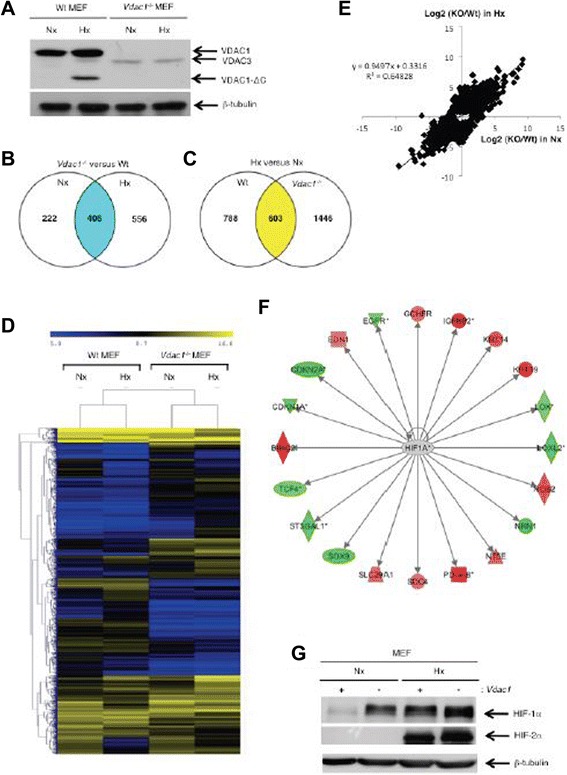
Characterization of wild-type (Wt) and VDAC1 null (Vdac1 −/−) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) in normoxia (Nx) and hypoxia 1 % O2 (Hx). a Wt and Vdac1 −/− MEF were incubated in Nx or Hx for 72 h and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for VDAC. β-tubulin was used as a loading control. mRNA was extracted from Wt or Vdac1 −/− cells after 72 h in Nx or Hx, and mRNA profiles were determined using pan-genomic microarrays. b Venn diagram depicting the numbers of genes significantly modulated between Wt vs Vdac1 −/− MEF in normoxia (Nx) or hypoxia (Hx). c Venn diagram depicting the numbers of genes significantly modulated between Hx and Nx in Wt or Vdac1 −/− MEF. d Heatmap comparing normalized log2 gene intensities of the top-ranked differentially expressed genes (1925 probes) for Wt and Vdac1 −/−MEF incubated in Nx or Hx (n = 2). The distance was measured using the Manhattan distance on the matrix of the log2 (intensity) and classification was performed using a complete agglomeration method. e Correlation between the change in the mRNA level between Wt and Vdac1 −/−MEF in normoxia and hypoxia. The determination coefficient (R2) was calculated using log2 fold changes from top modulated genes. f HIF-1α signaling pathway in normoxia in Vdac1 −/− MEF vs Wt MEF. Red and green color codes for up- and down-regulation, respectively. g Wt (+) and Vdac1 −/− (−) MEF were incubated in Nx or Hx for 72 h and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for HIF-1α and HIF-2α. β-tubulin was used as a loading control
