Figure 7.
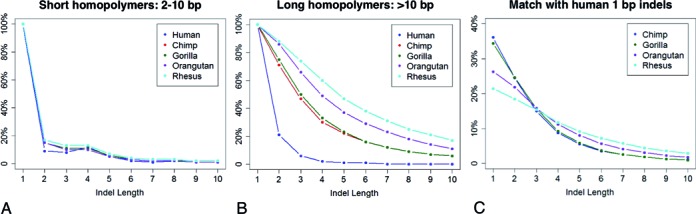
Comparison of indel length distribution across homopolymers in human and primate species. (A) Length distribution of indels located in short homopolymers (2–10 bp) in human and four primate species. The number of 1–10 bp indels was normalized to the number of 1 bp indels. The species are listed in an ascending order of the distance to human in the evolutionary tree, i.e. human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan and macaque. The fractions of indels of different length are consistent among the five species. (B) Normalized length distribution of indels in homopolymers over 10 bp long in human and four primates. The proportions of long indels have positive relation to the evolutionary distance between the human and primate. (C) Distribution of indel lengths in four primate species in homopolymers 10 bp or longer where human has 1 bp indel. The farther a primate species is located from human, the more biased the corresponding distribution is towards longer indels.
