Figure 1.
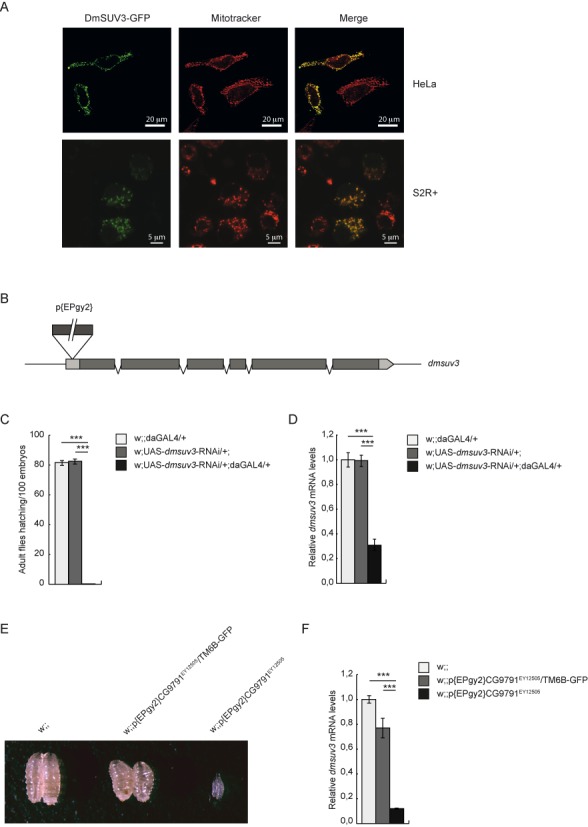
DmSUV3 is a mitochondrial protein essential for Drosophila melanogaster development. (A) HeLa and Schneider 2R+ cells expressing a GFP-tagged DmSUV3 fusion protein (DmSUV3-GFP) stained with mitotracker red CMXRos to visualize the mitochondrial network. Scale bars represent 20 μm (top panel) or 5 μm (bottom panel). (B) Schematic representation of the P-element insertion in the dmsuv3 gene. (C) Hatching rates in dmsuv3 knock down (w;UAS-dmsuv3-RNAi/+;daGAL4/+) and control (w;UAS-dmsuv3-RNAi/+; and w;;daGAL4/+) lines. (D) qRT-PCR of dmsuv3 transcript levels in knock down (KD) and control larvae at 5 days after egg laying (ael). RP49 transcript was used as endogenous control. All data are represented as mean ± SEM (***P < 0.001, n = 7). (E) Body size comparison in control (w;;), heterozygous P-element insertion (w;;P{EPgy2}CG9791EY12505/TM6B-GFP) and homozygous P-element insertion (w;;P{EPgy2}CG9791EY12505) larvae at 3 days ael. (F) qRT-PCR of dmsuv3 transcript levels in control, heterozygous P-element insertion and homozygous P-element insertion larvae at 3 days ael. RP49 transcript was used as endogenous control. All data are represented as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n = 5).
