Figure 1.
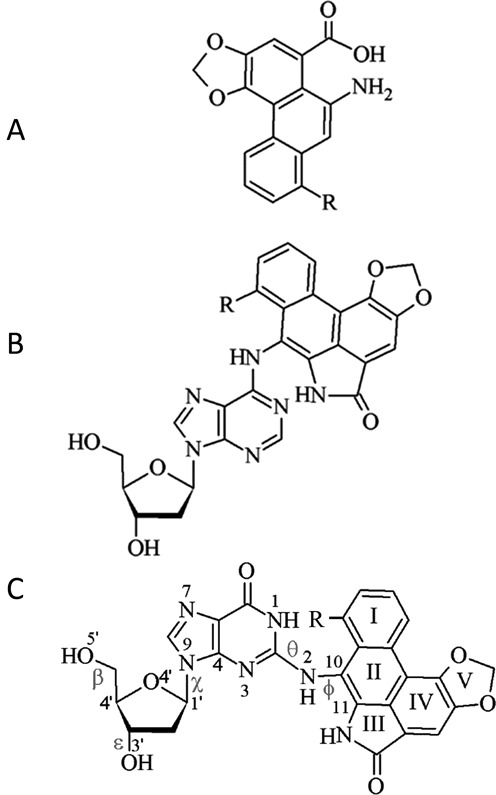
Structure of (A) aristolochic acids, as well as the corresponding (B) AL-N6-dA and (C) AL-N2-dG adducts (R = OCH3 for ALI and H for ALII). Definitions are provided for the θ (∠(N1C2N2C10)) and ϕ (∠(C2N2C10C11)) dihedral angles, which determine the orientation of the ALII moiety with respect to the base and χ (∠(O4′C1′N9C4)), which dictates the glycosidic bond orientation to be syn (90° > χ > −60°), high syn (120° > χ > 90°), anti (120° > χ > −90°) or high anti (−60° > χ > −90°). Dihedral angles β (∠(C4′C5′O5′H)) and ε (∠(C4′C3′O3′H)) govern the DNA sugar–phosphate backbone orientation.
