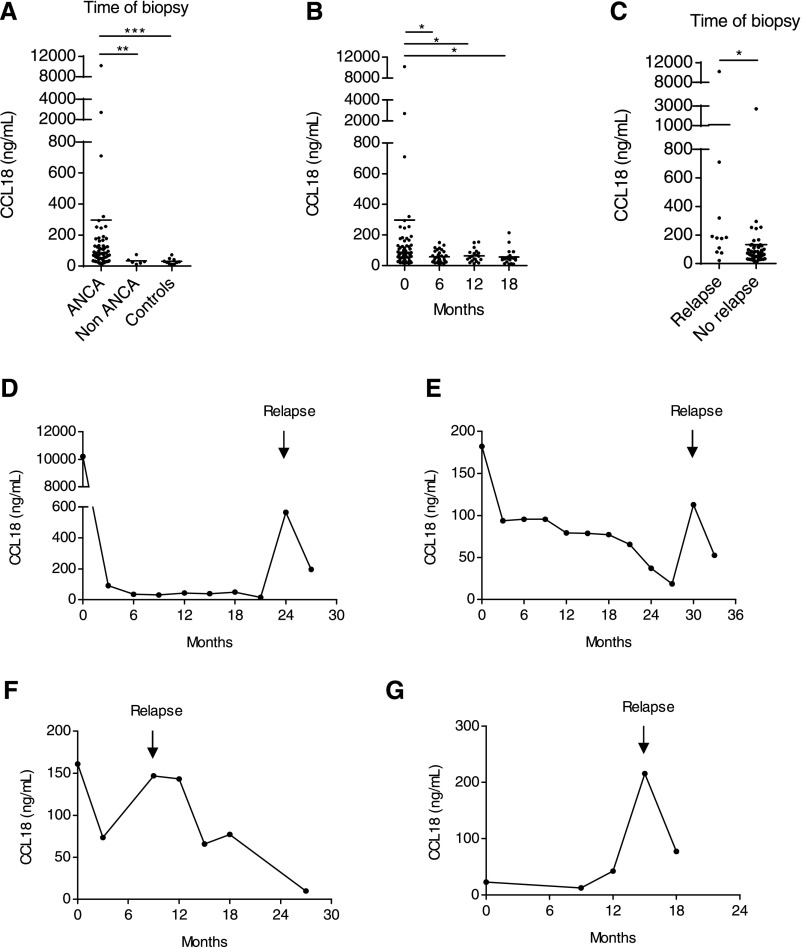
Figure 4.
CCL18 serum levels are elevated in ANCA-associated crescentic GN. (A) CCL18 serum levels were compared among patients with ANCA-associated crescentic GN (ANCA GN), patients with non-ANCA GN, and healthy volunteers (controls). The levels of CCL18 were determined by ELISA. CCL18 serum levels were markedly elevated in patients with ANCA GN (n=63) compared with patients with non-ANCA GN (n=6) and healthy controls (n=10). CCL18 serum levels did not differ among patients with non-ANCA GN and healthy volunteers. (B) CCL18 serum levels were measured during follow-up. CCL18 serum levels decreased during the initial immunosuppressive treatment with cyclophosphamide or rituximab and remained low during the maintenance therapy with azathioprine. The CCL18 measurements obtained at the time of diagnosis (n=63) and 6 (n=31), 12 (n=24), and 18 months of follow-up are shown (n=18). (C) At the time of biopsy, CCL18 levels were significantly higher in patients who experienced a renal relapse during follow-up (n=10) compared with those who remained in remission (n=53). (D–G) Longitudinal study with serum measurements of CCL18 in patients suffering from renal relapsing disease. Arrows indicate the onset of relapse. Bars represent means±SDs. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.