Fig. 2.
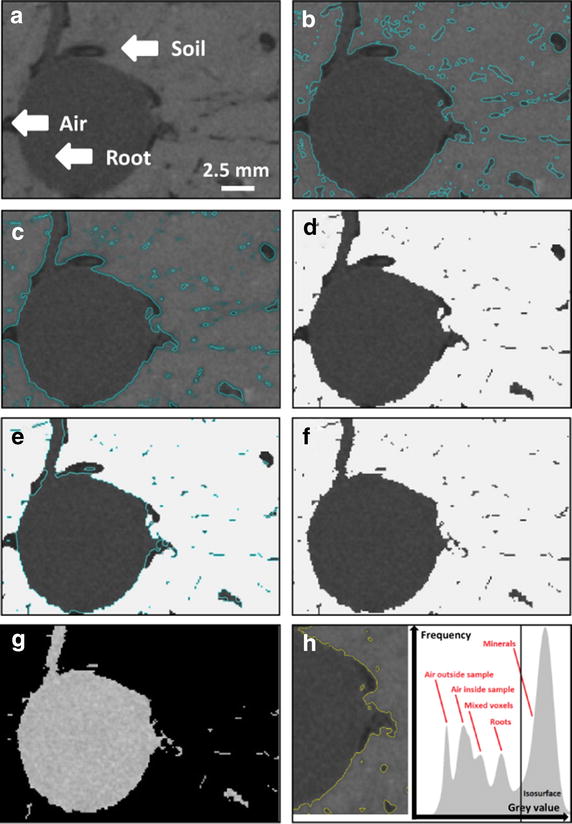
Steps of the segmentation protocol. Original X-ray CT volume of grass-legume mixture sample (details given in Table 1) showing roots, air-filled pores and soil (a). First step: advanced surface determination of the soil. The surface is shown as a blue line around the soil aggregates (b). Second step: dilatation of the region of interest (ROI), here 1 voxel, to add mixed voxels. The contour of the dilated surface is shown as a bright blue line (c). Step three: subtraction of the dilated ROI from a ROI containing the whole volume. Only roots and pores remain in the resulting volume (d). Step four: detection of the root surface (shown as a blue line) (e). Step five: the volume containing the roots and remaining noise (f) is exported to MatLab and filtered therein. The resulting, filtered volume containing only roots is shown in (g). The peaks of the gray values of air, mixed voxels, roots and minerals shown in the histogram are not completely separated (h)
