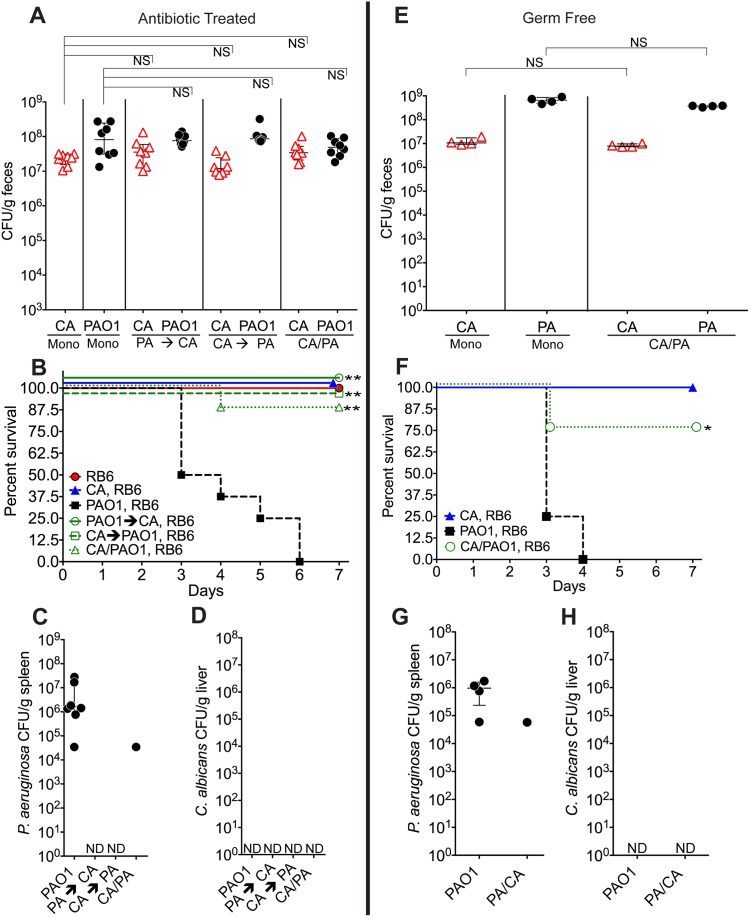
Fig 1. C. albicans inhibits P. aeruginosa virulence in mice.
A, E) C. albicans SC5314 (red triangles) and P. aeruginosa PAO1 (black circles) GI colonization levels in (A) adult antibiotic-treated mice (C3H/HeN) and (E) germ-free adult mice (C57BL/6). n = 8 per group for antibiotic-treated mice. n = 4 per group for germ-free mice. Points represent results from individual animals. Horizontal lines with bars represent the median with interquartile range. Statistical analysis performed by Mann-Whitney test. B, F) Survival curves of neutropenic antibiotic-treated (B) and germ-free (F) mice colonized with P. aeruginosa ± C. albicans. Mice were made neutropenic with intraperitoneal injection of 0.200 mg RB6-8C5 rat anti-mouse Ly-6G, Ly-6C monoclonal antibody. n = 8 for antibiotic-treated mice. n = 4 for germ-free mice. Statistical analysis performed by log-rank test. C, D, G, H) P. aeruginosa and C. albicans levels in spleens (C, G) and livers (D, H) of deceased neutropenic antibiotic-treated and germ-free mice colonized with P. aeruginosa ± C. albicans. Organ homogenates were plated on cetrimide, MacConkey (aerobic), TSA (aerobic,), BHI/Blood (anaerobic), and YVG (YPD agar with vancomycin and gentamicin) plates. The presence of a homogeneous population of green, oxidase-positive colonies on cetrimide agar and an absence of other bacterial growth on the MacConkey, TSA and BHI/Blood plates was used for confirmation of P. aeruginosa dissemination. The presence of a homogeneous population of creamy white colonies on YVG agar was used for confirmation of C. albicans dissemination. Points represent results from individual animals. Horizontal lines with bars represent the median with interquartile range. * p< 0.05; ** p<0.01; ns, not significant. CA, C. albicans. PA, P. aeruginosa. RB6, RB6-8C5 monoclonal antibody.