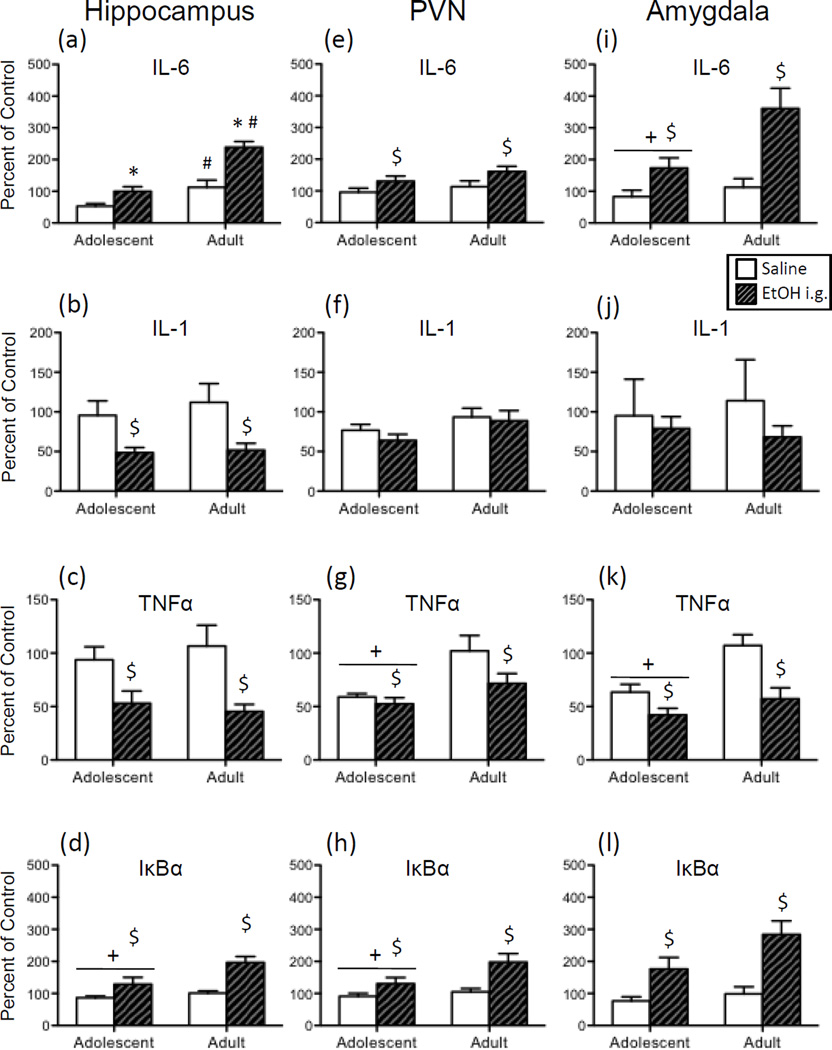
Figure 5.
Adolescent and adult male rats were given an acute intragastric (i.g.) challenge of tap water (white bars) or 4-g/kg ethanol (EtOH; 20% v/v; hatched bars), with brains collected for analysis three hours later. Interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), and nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (IκBα) gene expression was examined in the hippocampus (a, b, c, and d, respectively), paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) (e, f, g, and h, respectively), and the amygdala (i, j, k, and l). Data were calculated as a relative change in gene expression using the 2ΔΔC(t) method, with GAPDH used as a reference gene and the water-exposed adult animals serving as the ultimate control group. Bars denote group means ± standard error of the mean (represented by vertical error bars). Main effects of Age are signified by a horizontal line with a plus symbol (+), whereas main effects of Drug are indicated by a dollar sign ($) above the bar for each Age group. In the case of a significant Age x Drug interaction, asterisks (*) denote a significant effect of Drug within a given Age group, with the pound sign (#) indicating a significant difference between adolescents and adults within a Drug condition.