Fig. 4. The effect of synonymous mutations in poly(A) tracks of human genes.
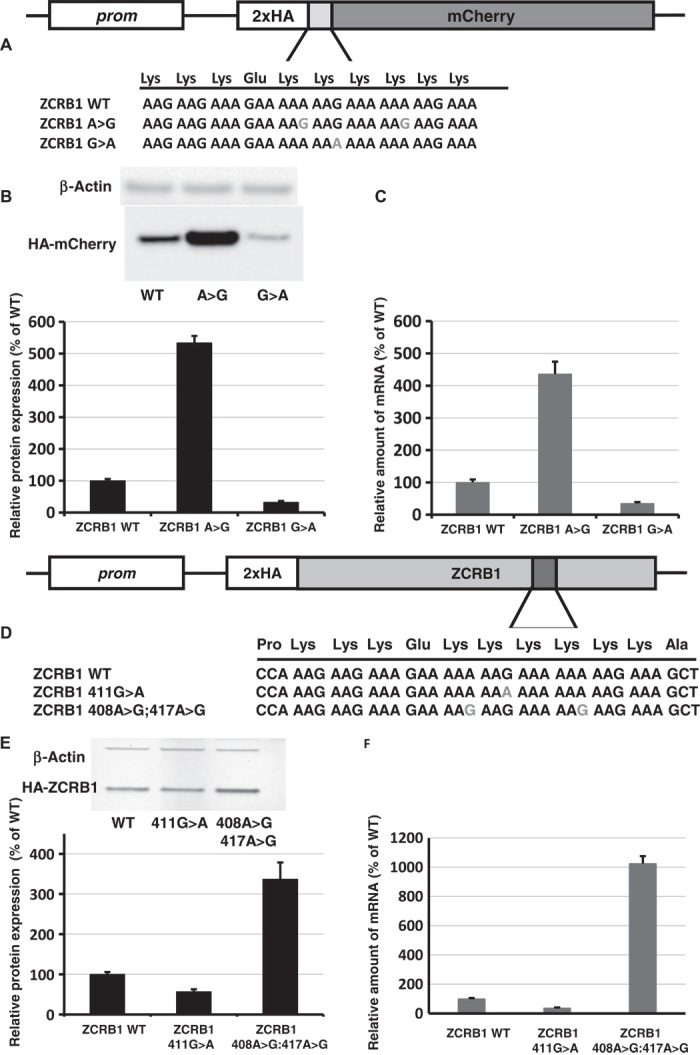
(A) Scheme of constructs with ZCRB1 gene poly(A) tracks used for analyses of synonymous mutations. (B) Western blot analyses and normalized protein expression of ZCRB1 reporter constructs with synonymous mutations (HA and β-actin antibodies). Each bar represents the percentage of wild-type ZCRB1-mCherry (WT) expression. (C) Normalized RNA levels of ZCRB1 reporter constructs with synonymous mutations. Neomycin resistance gene was used for normalization of qRT-PCR data. Each bar represents the percentage of wild-type ZCRB1-mCherry construct (WT) mRNA levels. (D) Scheme of full-length HA-tagged ZCRB gene constructs. Position and mutations in poly(A) tracks are indicated. (E) Western blot analysis and normalized protein expression of ZCRB1 gene constructs with synonymous mutations. Each bar represents the percentage of wild-type HA-ZCRB1 (WT) expression. (F) Normalized RNA levels of ZCRB1 gene constructs. Neomycin resistance gene was used for normalization of qRT-PCR data.
