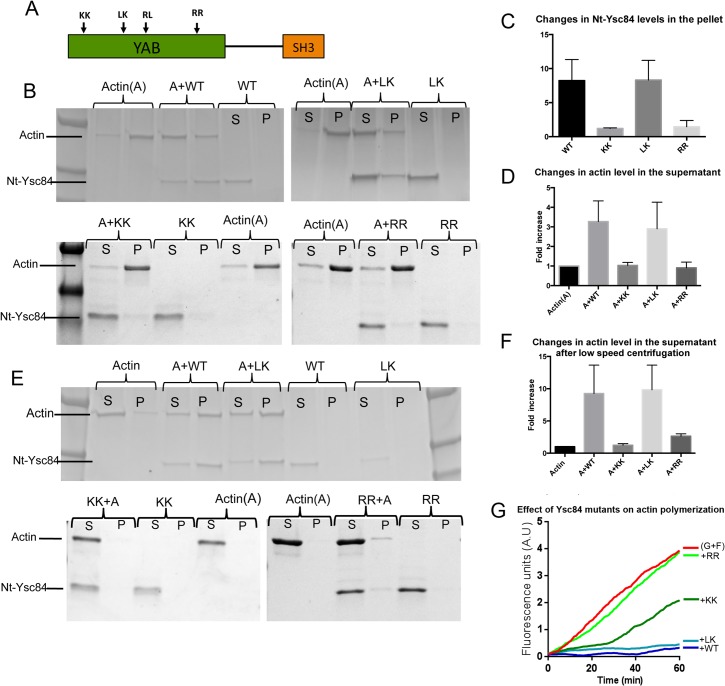
Fig 1. Generation of potential actin binding mutants in Ysc84 N-terminal YAB domain.
(A) Schematic diagram indicating the site of four conserved pairs of residues selected for mutation. (B) Wild-type and mutant Ysc84 proteins were purified and incubated in the presence or absence of actin during polymerization. Samples were centrifuged at high speed (90K) and supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions separated on gels. Data from at least three independent pelleting assays were combined to determine (C) the amount of Ysc84 itself that pellets with F-actin. Error bars are standard deviation; (D) the effect of Ysc84 on the level of actin that is in the supernatant fraction. (E) Pelleting assays were also performed by spinning samples of actin and Ysc84 at low speed (15K) to assess whether the proteins were able to bundle actin filaments. Supernatant and pellet fractions were separated on gels. (F) Data from at least three independent low speed pelleting assays were combined to determine the effect of Ysc84 on the level of actin that is in the pellet fraction. (G)The effect of Ysc84 wild type and the three purified mutant proteins on interaction with actin during polymerization in the presence of actin seeds (0.5 μM G-actin + 0.5 μM F-actin) using a pyrene actin fluorimetry assay. All Ysc84 proteins were added to the reaction at 0.6 μM.