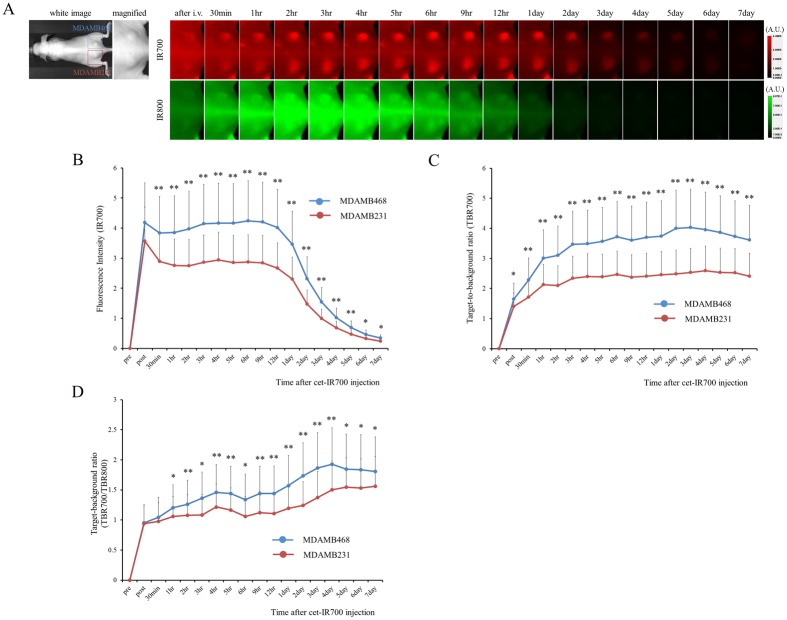
Fig 2. In vivo fluorescence imaging of MDAMB231 and MDAMB468 tumors.
(A) In vivo cet-IR700 and mouse IgG-IR800 fluorescence real-time imaging of bilateral (right dorsum; MDAMB468, left dorsum; MDAMB231) flank tumors in mice. The fluorescence intensity of cet-IR700 and mouse IgG-IR800 in both MDAMB231 and MDAMB468 tumor decreased gradually over days. The fluorescence intensity of IR700 was higher in MDAMB468 tumor compared with MDAMB231 tumor, while the fluorescence intensity of IR800 was almost same in both tumors. (B) Quantitative analysis of IR700 intensities in both tumors. The fluorescence intensities were significantly higher in MDAMB468 tumors compared with MDAMB231 tumors (n = 10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, by Mann-Whitney-U test). (C) Quantitative analysis of TBR in both tumors demonstrated differences between MDAMB468 tumors and MDAMB231 tumors (n = 10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, by Mann-Whitney-U test). (D) Quantitative analysis of TBR700/TBR800 in both tumors. Intensities were significantly higher in MDAMB468 tumors compared with MDAMB231 tumors (n = 10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, by Mann-Whitney-U test).