Figure 4.
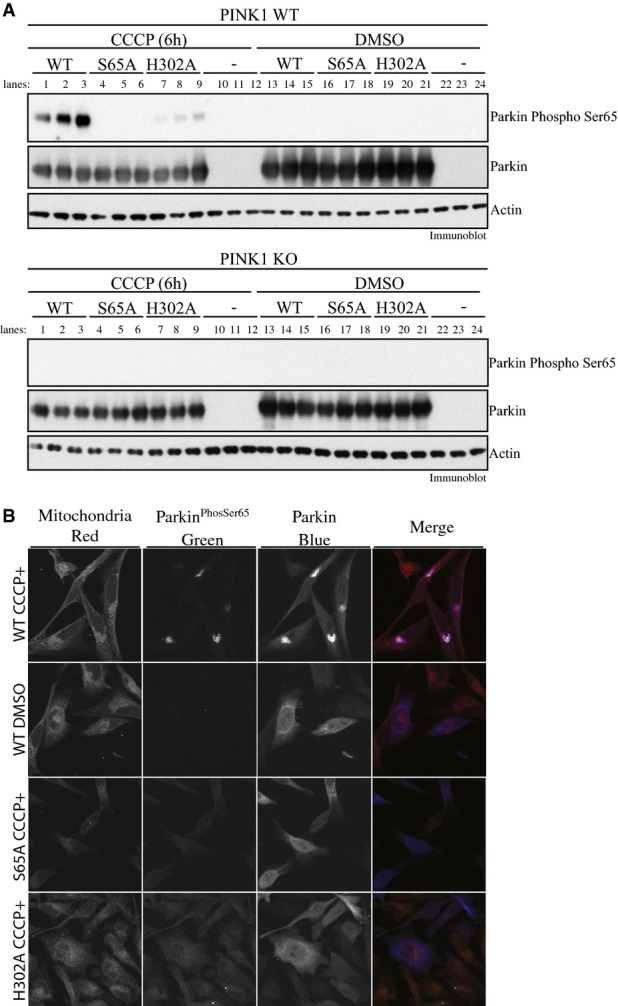
Parkin His302 is required for optimal phosphorylation of Parkin at Ser65 in cells upon CCCP-stimulated PINK1 activation
- Parkin H302A-mutant displays marked decrease in Parkin Ser65 phosphorylation upon PINK1 activation. Wild-type HeLa (upper panel) or PINK1 knockout HeLa cells (lower panel) were transfected with untagged wild-type (WT), and Ser65Ala (S65A)- or His302Ala-mutant Parkin and stimulated with 10 μM of CCCP or DMSO for 6 h in triplicates. The lysates were subjected to immunoblotting as follows: Parkin Ser65 phosphorylation (anti-phospho-Ser65 antibody), Parkin (anti-Parkin antibody), actin (anti-actin antibody) and PINK1 (anti-PINK1 antibody). Data are representative of three independent experiments.
- Parkin H302A-mutant disrupts mitochondrial accumulation of Parkin Ser65 phosphorylation. Wild-type HeLa cells stably expressing untagged wild-type (WT) (top row and second row), and Ser65Ala (S65A) (third row)- or His302Ala (H302A) (fourth row)-mutant Parkin were stimulated with 10 μM of CCCP for 6 h. HeLa cells expressing WT Parkin were also treated with DMSO for 6 h (second row). Cells were stained for Parkin Ser65 phosphorylation (anti-phospho-Ser65 antibody) or total Parkin (anti-Parkin antibody); mitochondria were labelled using MITO-ID® Red. Data representative of four independent experiments.
