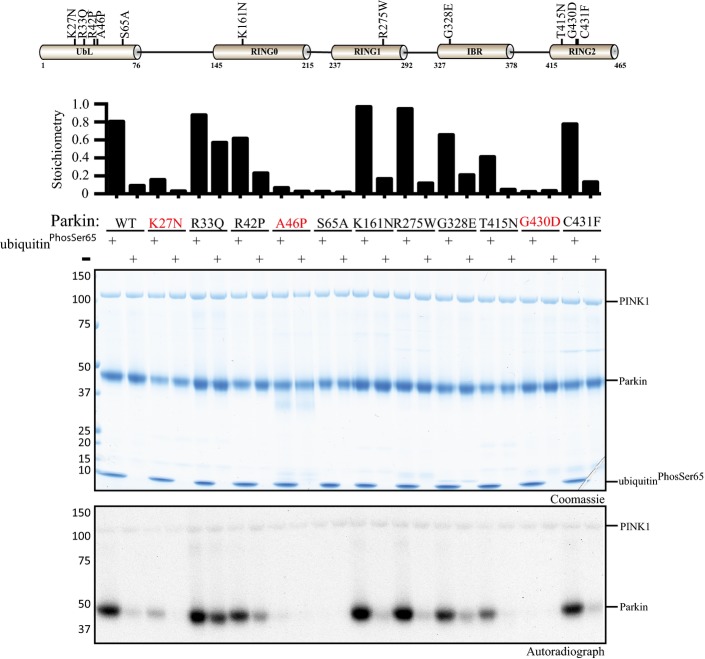
Identification of Parkinson’s disease-associated mutants that disrupt ubiquitinPhospho-Ser65-enhanced phosphorylation of Parkin by TcPINK1.
Schematic of Parkin domain and location of disease-associated Parkin mutants (upper panel). Wild-type (WT) full-length Parkin or the indicated disease point mutant was incubated with wild-type MBP-TcPINK1 and Mg2+ [γ-32P] ATP in the presence or absence of ubiquitinPhospho-Ser65. Proteins were detected by Colloidal Coomassie Blue staining (top panel) and Parkin phosphorylation levels assessed by incorporation of [γ-32P] ATP detected by autoradiography (bottom panel) and displayed above the panel (lower Panel).