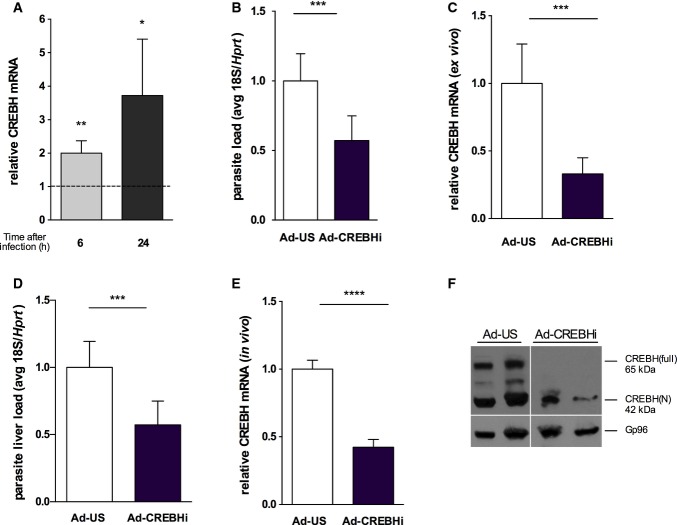
Figure 4.
CREBH knock-down, ex vivo and in vivo, restricts Plasmodium liver infection
- qRT–PCR analysis of hepatic Crebh mRNA in sorted Hepa 1.6 cells infected with P. berghei sporozoites and analysed at 6 and 24 h after infection relative to its GFP-negative control (dashed line) normalized to hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Hprt). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, t-test. Results are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 5 independent experiments).
- Plasmodium berghei infection quantification on mouse primary hepatocytes transduced ex vivo with adenovirus expressing a short hairpin RNA for Crebh (Ad-CREBH RNAi) and control adenovirus (Ad-US) by qRT–PCR for parasite 18S ribosomal RNA at 44 h after sporozoite delivery normalized to Hprt expression. Results are expressed as means ± SD, ***P < 0.001, t-test (n = 3 independent experiments).
- qRT–PCR analysis of Crebh mRNA in primary hepatocytes after Ad-US and Ad-CREBHi transduction normalized to Hprt expression. Results are expressed as means ± SD, ***P < 0.001, t-test (n = 3 independent experiments).
- Plasmodium berghei liver load quantification at 44 h after sporozoite delivery in mice transduced with Ad-US and Ad-CREBHi 48 h prior to infection by qRT–PCR for parasite 18S ribosomal RNA normalized to Hprt, ***P < 0.001, t-test. Results are expressed as means ± SD (n ≥ 4 mice per group, two independent experiments).
- qRT–PCR analysis of Crebh mRNA livers of mice transduced with Ad-US and Ad-CREBHi transduction normalized to Hprt expression. Results are expressed as means ± SD, ****P < 0.0001, t-test (n ≥ 4 mice per group, two independent experiments).
- Western blot analysis of CREBH precursor (CREBH-full) and the processed nuclear form (CREBH-N) of whole-liver lysates showing the complete absence of the precursor and a significant decrease in the processed form upon adenovirus-mediated CREBH knock-down (Ad-CREBHi). Gp96 served as a loading control.