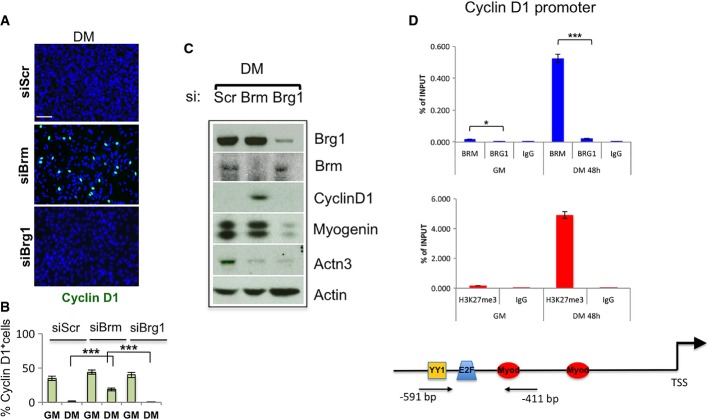
Figure 3.
Brm controls muscle differentiation-associated cell cycle arrest by repressing cyclin D1 expression
- A, B Immunofluorescence analysis of cyclin D1 expression in C2C12 cells depleted for Brm (siBrm) or Brg1 (siBrg1) in DM 48 h (A) and relative quantification reporting the percentage (%) of cyclin D1-positive cells (B). Scale bar, 50 μm. Data are presented as average ± SEM (n > 3). P-value was calculated using unpaired Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001. Experiments were performed at least three times.
- C Western blot analysis performed in siBrm, siBrg1, and siScr C2C12 cells cultured in GM or DM, using antibodies against Brm, Brg1, cyclin D1, myogenin, and Actn3. α-actin was used as a loading control. Experiments were performed at least three times.
- D Recruitment of Brg1 and Brm and analysis of H3K27me3 on a promoter sequence of the Ccnd1 gene in GM and DM. Arrows indicate the regions amplified by the primers used. Protein recruitment is expressed as relative enrichment of each factor compared to IgG after normalization for total input control (n = 3, error bars represent SEM). P-value was calculated using unpaired Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.