Figure 1.
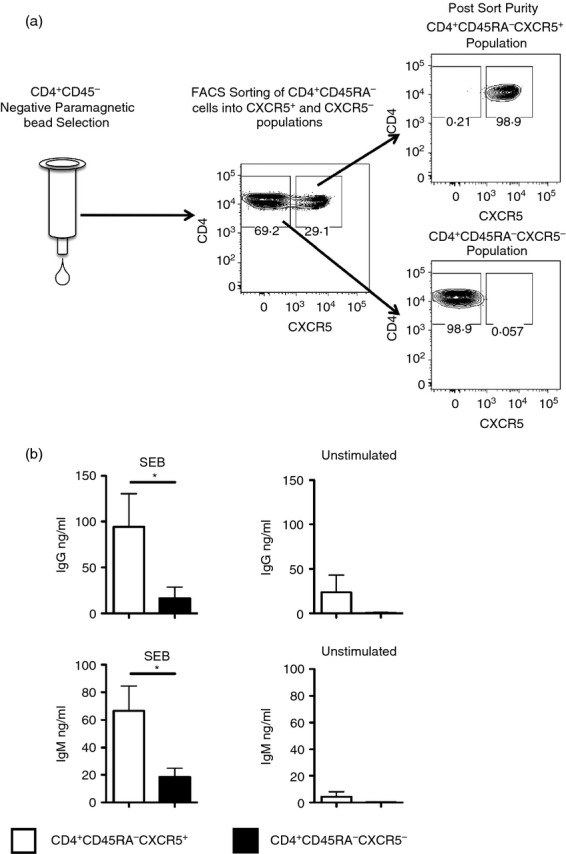
(a) Purification of CXCR5+ and CXCR5– memory CD4 T cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). PBMC from healthy human donors were enriched for CD4+ CD45RA– cells with negative paramagnetic bead selection. Pools of enriched cells were then stained for CD4, CD45RA and CXCR5. Stained cells were separated into CD4+ CD45RA− CXCR5+ and CD4+ CD45RA− CXCR5− cells. After sorting, the separated cells were typically > 98% pure. (b) B-cell help is concentrated within the CXCR5+ population of CD4+ CD45RA− human blood cells. Fifty thousand isolated CXCR5+ (open bars) or CXCR5– CD4+ CD45RA− T cells (filled bars) were cultured with 50 000 autologous naive B cells in the presence or absence of 500 ng/ml of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Day 10 culture supernatants were tested for total IgG and IgM by ELISA. The average levels of IgG (a) and IgM (b) in supernatant are shown from SEB-stimulated or unstimulated cultures, with the error bars representing the SEM. Data were analysed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and * indicates a P-value < 0·05.
