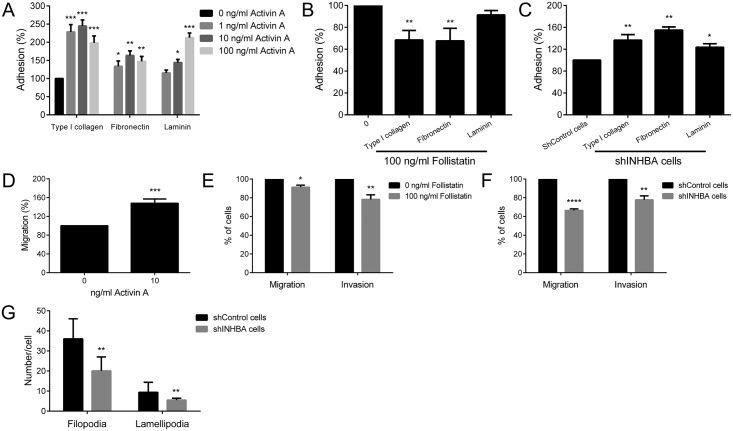
Fig 8. Activin A modulates the adhesion, migration and invasion of OSCC cells.
(A) Activin A treatment induced significantly the adhesion of HaCat cells on surfaces coated with type I collagen, fibronectin or laminin. (B) Follistatin decreased significantly the adhesion of SCC-9 ZsGreen LN-1 cells o surfaces coated with type I collagen and fibronectin. (C) Activin A knockdown augmented the adhesion to coated-surfaces, as revealed by significantly higher adhesion of shINHBA cells compared with shControl cells. (D) Activin A induced significantly the migration of HaCat cells, whereas follistatin blocked it and also reduced significantly the invasion of SCC-9 ZsGreen LN-1 cells through Matrigel-covered surfaces (E). (F) The migration and invasion of shINHBA cells were significantly lower in comparison with shControl cells. (G) Knock down of activin A interferes with cytoskeleton organization, reducing filopodia and lamellipodia formation. The number of filopodia and lamellipodia was significantly lower in shINHBA cells than in shControl cells. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.