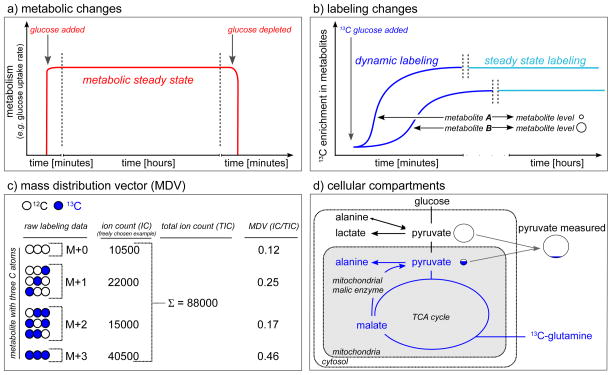
Figure 1.
Labeling basics. a) Time dependent metabolic changes: metabolism reaches a metabolic steady state when the parameters of interest (e.g. glucose uptake rate) are constant over time. b) Time dependent labeling changes: upon addition of an isotopically labeled carbon source, the isotopic enrichment will increase in the metabolites until the steady state enrichment is reached. c) Mass distribution vector (MDV) (also known as mass distribution (MID) vector): Labeling patterns are MDVs that consist of the fractional abundance of each isotopologue (mass isotopomer). M denotes mass of the unlabeled metabolite. d) Cellular compartmentalization: Most labeling pattern detection methods cannot resolve different cellular compartments, thus the whole cell average labeling pattern is measured.