Fig 3. Multiple sequence alignment of cyclophilin proteins from Triticum aestivum (TaCypA-1), Cajanus cajan (CcCyp), Camellia sinensis (CsCyp), Arabidopsis thaliana (AtCyp18-3, AtCyp19-2, AtCyp19-1, AtCyp18-4, AtCyp19-3, AtCyp20-3), Thellungiela halophila (ThCyp1), Oryza sativa (OsCyp2), Schistosoma mansoni (SmCypA) and Homo-sapiens (hCypA) was performed using clustalw2 server (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/).
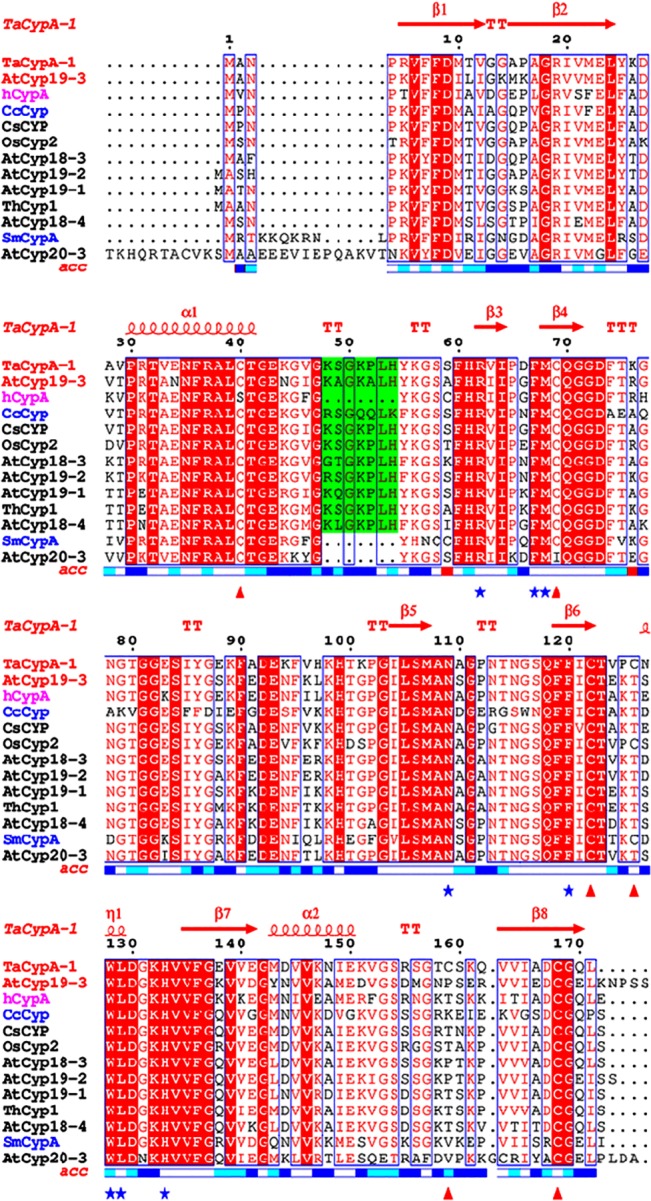
The ESPript 3.0 multiple-alignment editor (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/ESPript/) was used for the final presentation. The positions of the various α-helices and β-sheets in reference to the TaCypA-1 crystal structure (4HY7) are indicated at the top of the figure in red. Names of displayed cyclophilins sequences under investigation (AtCyp19-3 and TaCypA-1) have been colored red while for SmCypA and CsCyp are colored blue. Active site residues are marked by blue asterisks while the Cys residues corresponding to TaCypA-1 are marked with red triangles below the figure. The plant-specific divergent loop residues are shaded in green colour. Relative accessibility of amino acid is displayed below the alignment block (Blue: accessible, Cyan: intermediate and white: buried). The active site residues in all the sequences are very well conserved except for AtCyp19-1 for which a portion of protein sequence containing the first three active site residues and part of the divergent loop is deleted. Four Cys residues (C-40, C-69, C-122, C-168) have been conserved in all sequences except for Cys-40 in hCypA (mutated to S) and Cys 69 in AtCyp20-3 (mutated to I). TaCypA-1 has two additional Cys residues with the one corresponding to position 126 being also observed in OsCyp2 and SmCypA.
