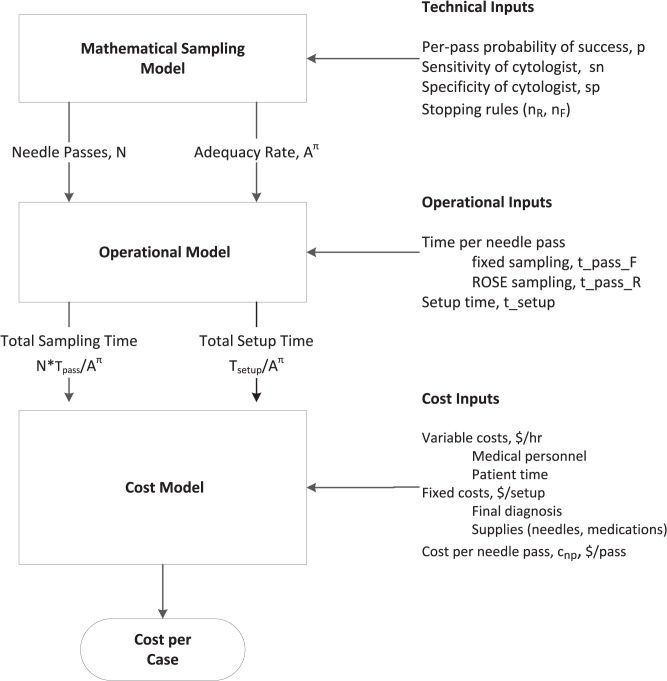
Fig 1. Sampling Algorithm.
The case starts with a setup period. Setup costs depend on the length of time, personnel and other resources used during setup. The length of the sampling period depends on the sampling protocol. Each sampling protocol depends on a stopping condition. For fixed sampling, sampling stops after a fixed number of needle passes. In ROSE sampling, sampling stops after the cytologist observes a required number of adequate samples. The length of the sample period depends on the number of needle passes and the time per needle pass. Two kinds of costs are incurred during sampling: costs related to time (personnel costs) and costs related to needle passes (supplies, adverse events). After sampling, the samples are processed and evaluated. The case ends if the samples are adequate for diagnostic assessment. Otherwise, the procedure is repeated.