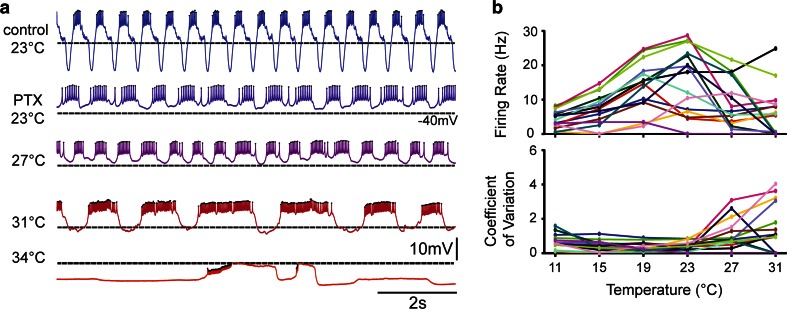
Fig. 2.
Effect of temperature on the activity of isolated LP neurons. a Example traces from one LP neuron. Control, LP is active in the intact network. After applying picrotoxin (PTX), glutamatergic connections to AB and PY are blocked and some residual PD inhibition is left. With increasing temperature, LP spike frequency increases and pauses between LP bursts become larger. At 34 °C LP “crashes”. b Firing rate in isolated LP neurons increases with increasing temperature. At 23 °C individual frequencies become more variable due to crashes. The coefficient of variation (ratio between the standard deviation and the mean of the spike frequency) increases at higher temperatures, due to variable spiking patterns in individual LP neurons. N = 15 LP neurons; each color represents one LP neuron