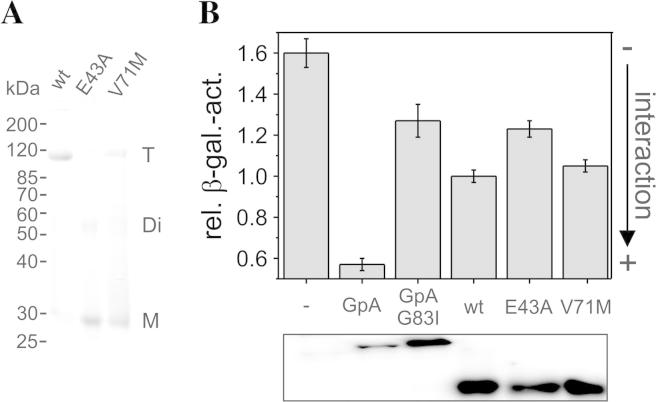
Fig. 2.
In vitro and in vivo oligomerization of GlpF-wt, GlpF-E43A and GlpF-V71M. (A) Semi-native SDS–PAGE analysis of purified GlpF-wt and the GlpF mutants E43A and V71M (T: tetramer, Di: dimer; M: monomer). 7.5 μg protein was loaded per lane. (B) The oligomerization tendency of the GlpF-wt, GlpF-E43A, and GlpF-V71M was assessed using the GALLEX assay. As controls, the rel. β-gal. activities of the wt and G83I-mutated GpA TM domains, that possess a strong and weak dimerization propensity, respectively, as well as the rel. β-gal. activity determined in cells transformed with the empty expression plasmid (−) were determined. The determined interaction propensity of GlpF-wt was set at 1.0. For the Western blot analysis shown in the lower panel an antibody recognizing the LexA DNA binding domain was used.