Figure 1.
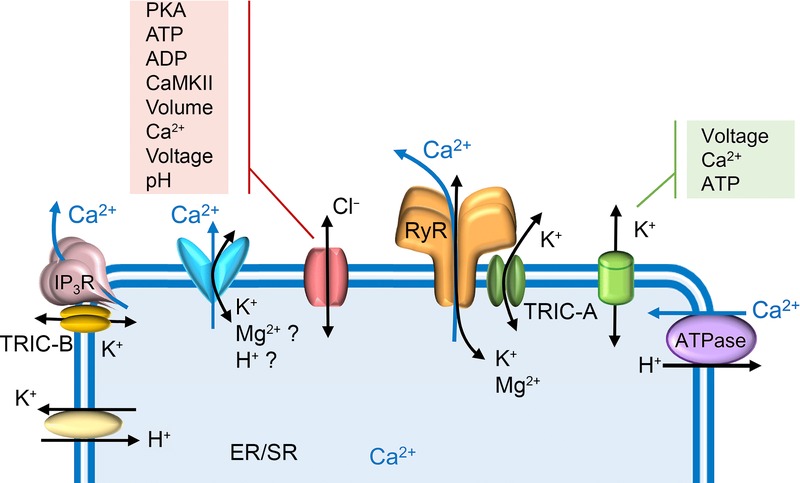
Ionic fluxes across the ER/SR compartment
RyR and IP3R are the acknowledged Ca2+ release channels of the ER/SR. The sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) pumps Ca2+ into ER/SR with counter movement of H+ out. There are also numerous unidentified ionic pathways that are predicted from experimental work. These comprise the various SR anion and cation channels which appear to be triggered by many distinct activators. In addition, a putative ER/SR-residing K+–H+ exchanger may be responsible for pumping protons into the SR in exchange for K+ moving out. Many recognised ion channels are also located on ER/SR membranes although their physiological roles in this location have not been clearly assigned. These include the monovalent cation-conducting TRIC channels and several non-selective cation channels (for example, MG23, pannexins, presenilins and the TRP channels, TRPV1, TRPP2 and TRPM8), often described as Ca2+ leak channels.
