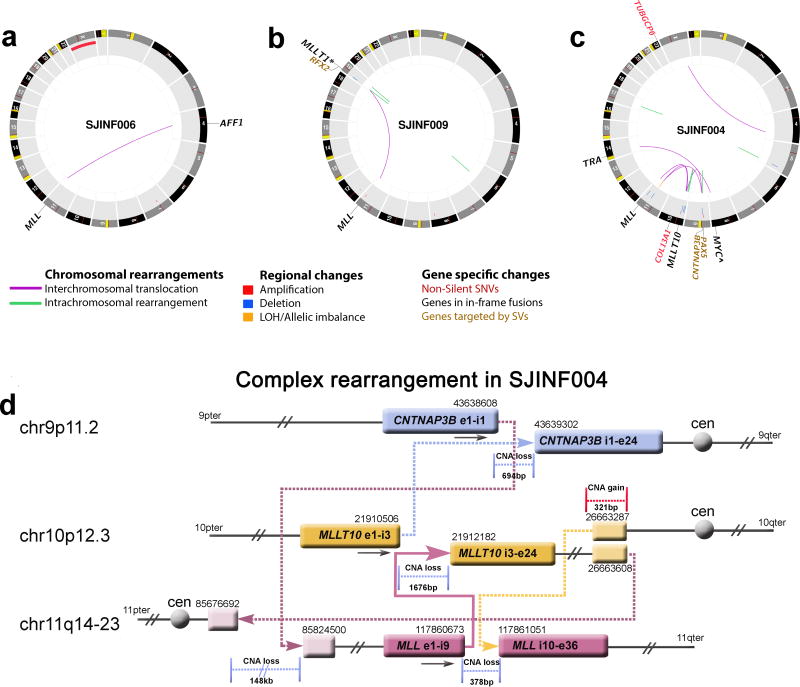
Figure 1.
Somatic mutations detected by whole genome sequencing of infant MLL-R ALL. (a–c) CIRCOS plots of somatic non-silent mutations in three infant MLL-R ALL cases. (a) INF006 contained a balanced t(4;11)(q21;q23) encoding the MLL-AFF1 and gain of chromosome X. (b) INF009 contained a balanced t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) with the break on chromosome 19 occurring 22.7kb 5` of MLLT1 resulting in a spliced in-frame MLL-MLLT1 chimeric gene. The translocation had an inverted intrachromosomal duplication spanning 0.3kb at the breakpoint on chromosome 19 that resulted in an out-of-frame RFX2-MLL fusion. In addition, an unrelated intrachromosomal deletion of 46bp was detected on chromosome 6. (c) INF004 contained a complex three-way translocation involving chromosomes 9, 10, and 11 that encoded the MLL-MLLT10 on the derivative chromosome 11, an out-of-frame MLLT10-CNTNAP3B chimeric gene on chromosome 9, and a truncated 3` MLL on chromosome 10. The case also contained a t(8;14)(q24;q11.2) that resulted in the juxtaposition of MYC to the T-cell antigen receptor alpha (TRA) gene as denoted by the ∧. In addition, a non-silent SNV in COL13A1 and a deletion on chromosome 9 disrupted PAX5. (d) Structure of the INF004 complex translocation involving chromosomes 9p11 (blue), 10p12 (yellow), and 11q14–23 (burgundy). The genomic coordinates (hg18) are indicated above each genomic segment. The MLL-MLLT10 fusion gene is depicted by the solid arrow and all other rearrangements by dotted arrows. Copy number gains (red) and losses (blue) at the respective break points are shown. The final genomic products on chromosomes 9, 10 and 11 are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9. Ter, terminus; Cen, centromere.