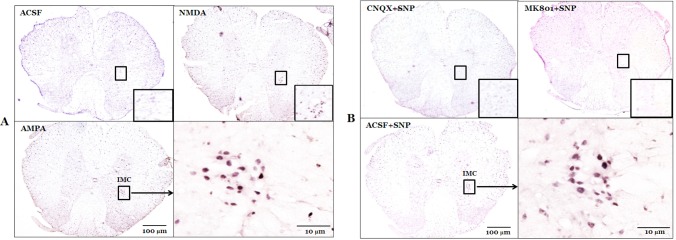
Fig. 1. Photomicrographs showing the effect of medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) glutamate on c-Fos protein expression in the spinal cord. (A) Effect of microinjection of glutamate receptor agonists into the left MVN on c-Fos protein expression in the intermediolateral cell column (IMC) of the T7 spinal cord. (B) Effect of pretreatment with microinjection of glutamate receptor antagonists into the left MVN on c-Fos protein expression in the IMC of the T7 spinal cord. Right lower quadrant in A and B represents higher magnification. Rectangles in right lower corner of each diagram represent higher magnification. ACSF, microinjection of artificial cerebrospinal fluid into the MVN; NMDA, microinjection of NMDA into the MVN; AMPA, microinjection of AMPA into the MVN; ACSF+SNP, SNP infusion after pretreatment with ACSF in the MVN; MK801+SNP, SNP infusion after pretreatment with MK801 in the MVN; CNQX+SNP, SNP infusion after pretreatment with CNQX in the MVN. ACSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; AMPA, 2-amino-3-(5-methyl-3-oxo-1,2-oxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid; CNQX, 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione; IMC, intermediolateral cell column; MK801, (+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d] cyclohepten-5,10-imine maleate; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; SNP, sodium nitroprusside.