Table 10.
R and S l-type doublings for C6H6, (in cm−1)
| Const. | Modes | This work | Lit. | Const. | Modes | This work | Lit. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 7 | 6 | 0.10 | — | S | 18 | 8 | 0.60 | 0.64 |
| S | 8 | 6 | 0.19 | 0.27 | S | 18 | 9 | −1.50 | −1.56 |
| R | 8 | 7 | 0.18 | — | S | 18 | 10 | −10.09 | −10.26 |
| S | 9 | 6 | −0.11 | — | R | 18 | 16 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| R | 9 | 7 | 0.32 | 0.26[a] | R | 18 | 17 | −0.26 | −0.39 |
| R | 9 | 8 | −0.72 | −0.78 | S | 19 | 6 | 1.51 | 1.92 |
| S | 10 | 6 | 0.61 | 0.71 | R | 19 | 7 | 0.03 | −0.09 |
| R | 10 | 7 | 0.04 | — | R | 19 | 8 | −0.60 | −0.39 |
| R | 10 | 8 | 0.68 | 0.70 | R | 19 | 9 | −0.21 | −0.20 |
| R | 10 | 9 | −1.66 | −1.84 | R | 19 | 10 | 0.03 | — |
| R | 16 | 6 | −0.01 | — | S | 19 | 16 | 0.69 | 0.68 |
| S | 16 | 7 | −0.13 | — | S | 19 | 17 | −0.33 | −0.33 |
| S | 16 | 8 | −0.53 | −0.49 | S | 19 | 18 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| S | 16 | 9 | 0.62 | 0.64 | S | 20 | 6 | −0.71 | −0.35 |
| S | 16 | 10 | 0.33 | 0.34 | R | 20 | 7 | 0.05 | — |
| R | 17 | 6 | −0.09 | — | R | 20 | 8 | −0.24 | −0.21 |
| S | 17 | 7 | 0.05 | — | R | 20 | 9 | −0.28 | −0.30 |
| S | 17 | 8 | −0.71 | −0.68 | R | 20 | 10 | 0.75 | 0.85 |
| S | 17 | 9 | 0.13 | 0.10 | S | 20 | 16 | 0.19 | 0.23 |
| S | 17 | 10 | −0.44 | −0.47 | S | 20 | 17 | 0.04 | — |
| R | 17 | 16 | −0.40 | −0.46 | S | 20 | 18 | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| R | 18 | 6 | 0.59 | 0.77 | R | 20 | 19 | −0.50 | −1.21 |
| S | 18 | 7 | −0.02 | — | |||||
Calculations at the B3LYP/SNSD level, with resonant terms treated within the DVPT2 approach. The reference values are calculated at the B3LYP/TZ2P level, from Table 6 of Ref.172.
Note that in the reference the values are reported as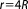 and
and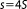 .
.
indicates that the value corresponds with the one reported between parentheses in Ref.172.
