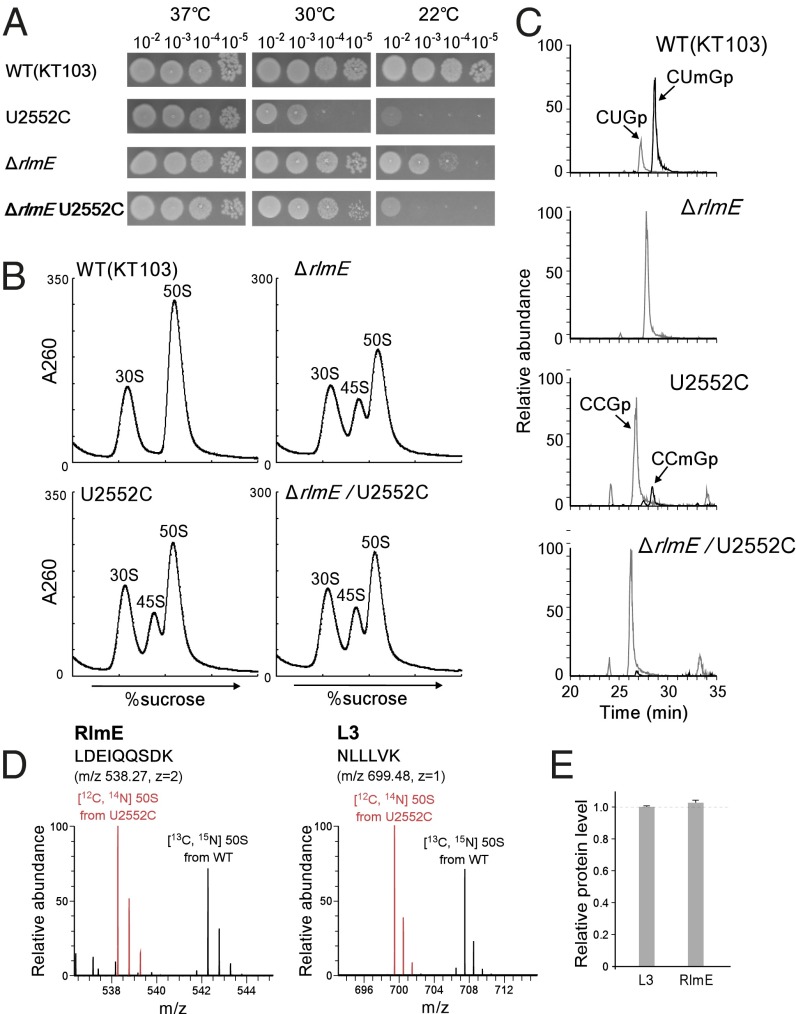
Fig. 3.
Characterization of the U2552C mutant. (A) Growth properties of a series of KT103 strains. Overnight full-growth cultures of WT (Top), U2552C mutant (Second Panels), ΔrlmE (Third Panels), and ΔrlmE/U2552C (Bottom) were serially diluted (102- to 105-fold dilutions), spotted onto LB plates, and cultivated at 37 °C for 18 h (Left), 30 °C for 24 h (Middle), or 22 °C for 50 h (Right). (B) SDG profile of ribosomes from a series of KT103-derived strains: WT KT103 (Upper Left), U2552C mutant (Lower Left), ΔrlmE (Upper Right), and ΔrlmE/U2552C (Lower Right) were cultured at 37 °C until OD600 reached ∼0.4, cultivated at 22 °C for 100 min, and then analyzed by SDG at low Mg2+ concentration. (C) Mass-spectrometric analysis of 2′-O-methylation at position 2552 in 23S rRNAs from a series of KT103-derived strains: WT (Top), ΔrlmE (Second Panel), U2552C mutant (Third Panel), and ΔrlmE/U2552C (Bottom). The mass chromatograms represent CUmGp (m/z 987.13; black line), CUGp (m/z 973.12; gray line), CCmGp (m/z 986.15; black line), and CCGp (m/z 972.13; gray line) from the RNA segment G2529–C2579 of the 23S rRNAs. (D) SILAC quantitation comparing the level of RlmE bound to U2552C 50S relative to WT 50S. Left and Right panels show mass spectra of tryptic peptides from RlmE and L3, respectively. Red and black signals represent protonated ions of unlabeled peptides from the U2552C mutant 50S and [13C6, 15N2] lysine-labeled corresponding peptides from WT 50S, respectively. Sequences, mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), and charge state (z) of the peptides are indicated. (E) Level of RlmE bound to U2552C 50S relative to WT 50S. The intensity ratio of RlmE-derived peptides between U2552C and WT 50S was normalized to that of L3-derived peptides. Average values with SD of the intensity ratios of three tryptic peptides of RlmE and L3 (Table S1) were obtained.