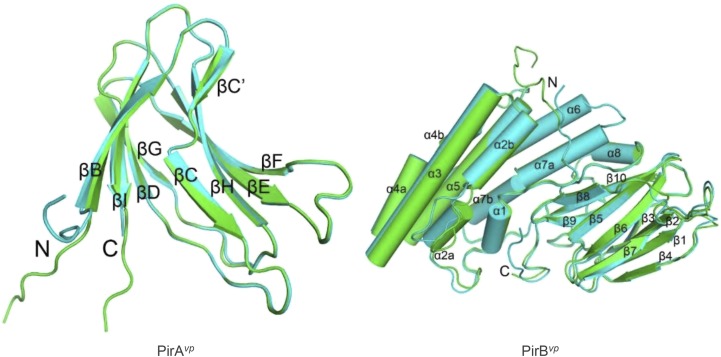
Fig. S8.
Overall structure of PirAvp and PirBvp. The two asymmetric monomers of PirAvp (Left) and PirBvp (Right) are superimposed and colored in green and cyan. Arrows and cylinders represent β-strands and α-helices, respectively. All secondary structural elements are labeled, and the N and C termini are shown. PirAvp folds into an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel with jelly-roll topology as seen in viral capsid proteins, and composed of the BIDG and CHEF β-sheets. A large β-bulge was found in strand C. PirBvp folds into an N domain with seven α-helices and a C domain with 10 β-strands. Helix α1 is short, and helices α2, α4, and α7 are kinked. A large loop insertion was found in the middle of helix α2. Strands β1–β4 and β5–β8 of the C domain constitute two antiparallel sheets in a wedge-like formation, and the long β9–β10 ribbon intercalates between the two β-sheets on the proximal side near the N domain. The N and C domains are connected by a long loop of more than 40 residues, which includes a short helix (α8). The N-terminal segments of both PirAvp and PirBvp are flexible. Except for the N terminals, the two monomers of PirAvp show an rmsd of 0.25 Å for 101 Cα atoms, and those of PirBvp differ by an rmsd of 0.76 Å for 412 Cα atoms. The inserted loop in α2 deviates by 3.3–5.4 Å.