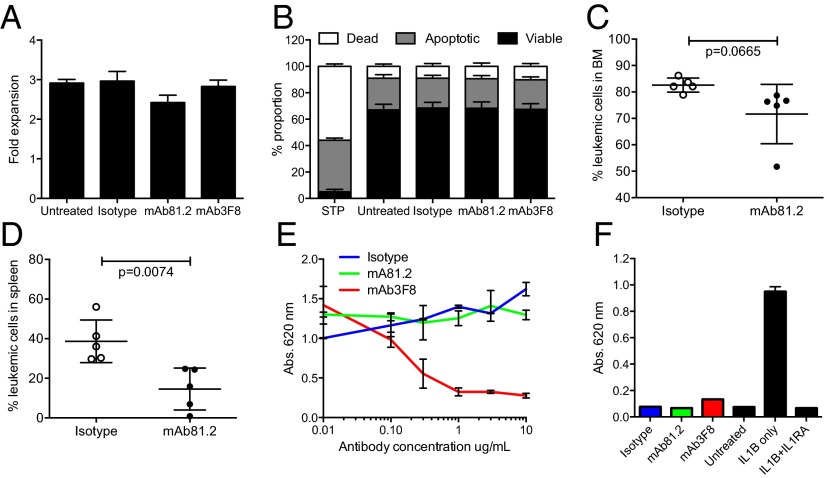
Fig. 2.
Antileukemic in vivo effect on MA9Ras cells depends on murine effector cells. (A) Fold expansion of MA9Ras cells in suspension cultures with addition of 10 μg/mL IL1RAP-targeting antibodies mAb81.2 and mAb3F8 or an isotype control antibody (means ± SEM from four experiments with technical duplicates). (B) Relative levels of viable, apoptotic, and necrotic MA9Ras cells after treatment with 10 μg/mL mAb81.2, mAb3F8, or an isotype control antibody. Staurosporine treatment (STP) was used as positive control for apoptosis (means ± SEM from three experiments with technical duplicates). (C and D) NSG mice were engrafted with MA9Ras cells and treated with mAb81.2 or an isotype control antibody (n = 5 in both groups). Graphs show BM (C) and spleen (D) leukemic cell frequency at death 39 d after transplantation (means ± SD). (E) IL-1 activates NF-kβ in the HEKblue IL1R1 reporter cell line. The graph shows the NF-kβ activation measured by absorbance in the presence of IL-1 upon addition of mAb81.2 or mAb3F8 or an isotype control antibody (means ± SEM from technical duplicates; one representative experiment out of three). (F) Absorbance of NF-kβ activation in the HEKblue IL1R1 reporter cell assay in the absence of IL-1 with IL1RA included as a control (one representative experiment out of three). P values were calculated with Student’s t test.