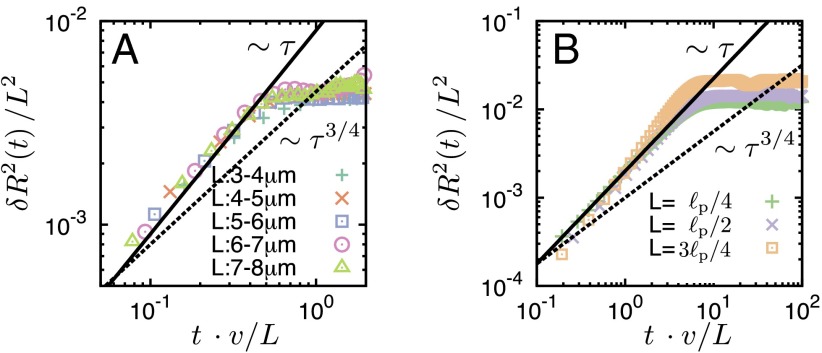
Fig. 4.
MSD of the end-to-end distance of a filament, (rescaled by ) vs. time t (rescaled by ). (A) Experiments were performed for filaments with the length range 3–8 μm. To achieve sufficient statistical power, we averaged over a large number of filaments and, in addition, performed a moving time average (Materials and Methods). The typical relaxation time is 0.5 s, which implies for a filament speed of 6 μm/s that the filament must move approximately half its length before bending modes are relaxed. (B) Results obtained from the computational model for different values of as indicated in the graph. Experiment and computer simulations both show that relaxation of bending modes for active filaments is independent of filament length L, and that with an exponent , which significantly deviates from Brownian scaling with . There are differences in the absolute scale, which we attributed to the simplification of the motor dynamics and the motor-filament interaction. Parameters: corresponding to a linear motor density of .