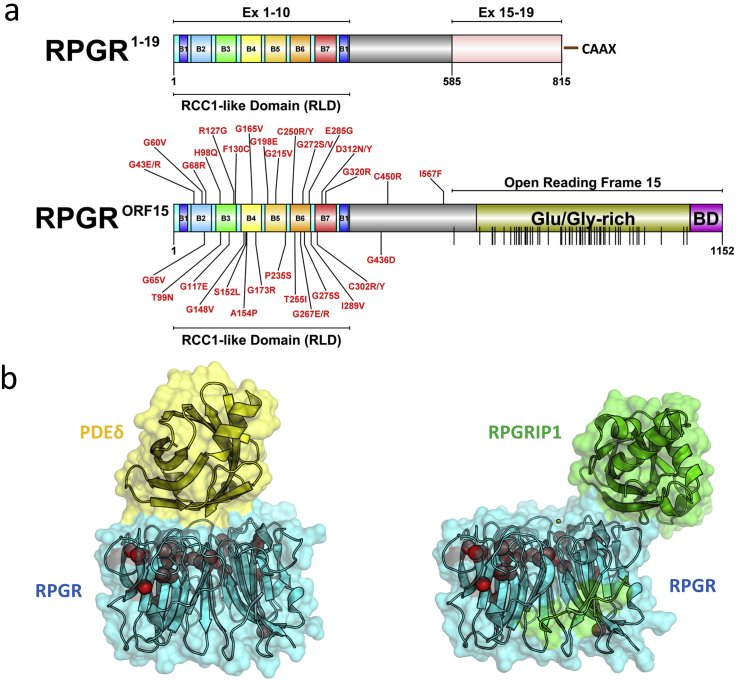
Fig. 1.
Major RPGR protein isoforms (constitutive RPGREx1-19 and RPGRORF15) domain schematic. (a) Domain architecture schematics for both major isoforms are shown drawn to scale. The seven blades (B1 to B7) that form the beta-propeller RCC1-like domain (RLD) encoded within Exons 1–10 in both major isoforms are indicated. The RPGREx1-19 C-terminal isoprenylation site (CAAX) is shown. The location of the RPGRORF15 Glutamate/Glycine-rich Domain and Basic Domain (BD) within the Open Reading Frame 15 are highlighted. All known disease-causing missense mutations (labelled), and a total of 52 known nonsense mutations specifically located within the Open Reading Frame 15 (vertical lines on domain schematic) are indicated. Mutation data was mapped from the Human Gene Mutation Database (Stenson et al., 2014) (accessed 27th May 2015). (b) The crystal structures of the RPGR RLD (blue) in complex with PDEδ (yellow) (Wätzlich et al., 2013) and RPGRIP1 (green) (Remans et al., 2014) are shown using PyMol (http://www.pymol.org) as surface representations with a transparency setting to highlight location of known missense mutations (red spheres, only alpha carbon atoms shown) on structure. PDEδ and RPGRIP1 interaction sites on the surface RPGR partially overlap (Remans et al., 2014).