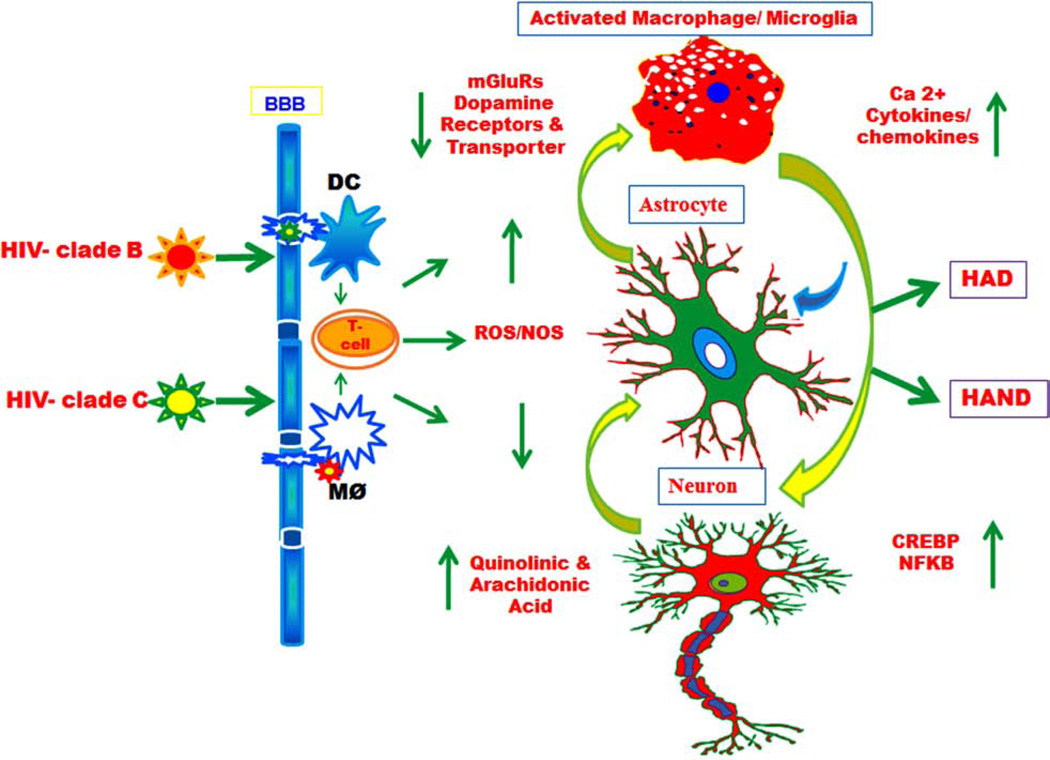
Fig. (5).
Schematic pathway of HIV-1 B and C differentially influence central nervous system. A comprehensive model showing how HIV-1 clade B and C differentially impact signaling through dendritic cells (DC), T cell and macrophages (and the closely related microglial cells) in the brain and their contribution to the pathogenesis of AIDS Dementia Complex (ADC) and neurocognitive disorders (HAND). The viral Trans activator protein (Tat) leads to secretion of neurotoxin QUIN and Arachidonic acid metabolites mediators’ which influence dopamine and mGlu receptor can activate astrocytes, and that may damage neurons differentially.