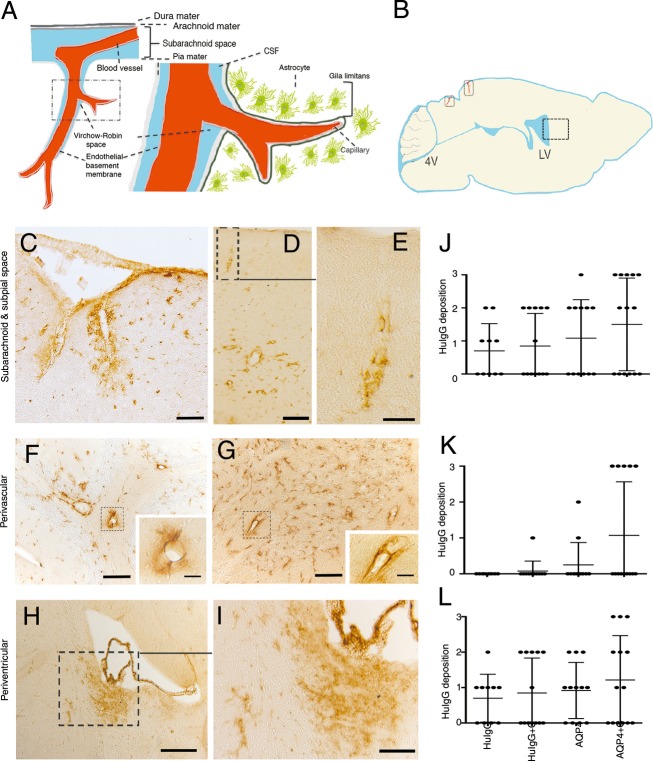
Figure 1.
Distribution of AQP4-IgG from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the brain parenchyma. (A) Subpial vasculature in relation to subarachnoid space and brain parenchyma, showing relevant anatomical structures including the pial vessel, subarachnoid space, the Virchow-Robin space and the subpial glia limitans surrounding penetrating vessels into the brain, in schematic form. (B) A mouse brain in sagittal section showing a diagram of the intrathecal distribution of human IgG in this study. Areas of penetrating vessels into the brain are marked with rectangles. (C–K) Sagittal sections of the brain of animals after intrathecal injection of AQP4-IgG + complement into the cisterna magna. Sections were stained for human IgG. (C) Micrographs show distribution of AQP4-IgG in the brain parenchyma around surface pial vessels in subarachnoid and subpial spaces, surrounding penetrating vessels into the brain in midbrain (superior colliculus, midbrain), (D) and in a cortical region proximal to the hippocampus, (E) shows a magnified view of an area in (D) with a penetrating vessel into the brain. (F) Perivascular deposition of AQP4-IgG at brain parenchymal vessels distal from the site of parenchymal entry of pial vessels in cerebellum and (G) midbrain. (H) periventricular deposition of AQP4-IgG at the lateral ventricles and (I) Magnified view of an area from (H). (J–L) HuIgG deposition of varying intensity from groups of mice treated 2 days previously by intrathecal injection of AQP4-IgG + complement (n = 14), AQP4-IgG alone (n = 12), control HuIgG (n = 10), control HuIgG + complement (n = 13). Histological grading as mild (+ = 1), moderate (++ = 2) or intense (+++ = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD, (J) Paravascular route deposition (K) Perivascular deposition at brain parenchymal vessels distant from the site of parenchymal entry of pial vessels (L) Periventricular deposition. Bar 50 μm (C, F, and G), 20 μm (inserts F, G, and E), 100 μm (D and I), 200 μm (H).