Abstract
Purpose: Official guideline published and coordinated by the German Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics (DGGG). Positioning injuries after lengthy gynecological procedures are rare, but the associated complications can be potentially serious for patients. Moreover, such injuries often lead to claims of malpractice and negligence requiring detailed medical investigation. To date, there are no binding evidence-based recommendations for the prevention of such injuries. Methods: This S1-guideline is the work of an interdisciplinary group of experts from a range of different professions who were commissioned by DGGG to carry out a systematic literature search of positioning injuries. Members of the participating scientific societies develop a consensus in an informal procedure. Afterwards the directorate of the scientific society approves the consensus. The recommendations cover:
Key words: gynecologic operations, positioning injuries, prevention
Abstract
Zusammenfassung
Ziel: Offizielle Leitlinie, publiziert und koordiniert von der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe (DGGG). Lagerungsschäden nach langdauernden gynäkologischen Eingriffen sind seltene aber für die Patientin potenziell schwerwiegende Komplikationen. Zudem sind sie nicht selten Anlass für medizinische Gutachten und gerichtliche Auseinandersetzungen. Bis dato existieren keine verbindlichen, evidenzbasierten Empfehlungen zur Prävention. Methoden: Die vorliegende S1-Leitlinie ist das Ergebnis der Arbeit einer interdisziplinären und interprofessionellen Expertengruppe, die im Auftrag der Leitlinienkommission der DGGG eine systematische Literaturrecherche zum Thema durchgeführt hat. Mitglieder der beteiligten Fachgesellschaften entwickeln in einem informellen Prozess einen Konsensus. Anschließend bestätigen die Direktorien der Fachgesellschaften diesen Konsensus. Die Empfehlungen berücksichtigen:
Schlüsselwörter: gynäkologische Eingriffe, Lagerungsschäden, Prävention
I Guideline Information
DGGG Guidelines Program
Information on this topic is provided at the end of the guideline.
Citation format
The prevention of positioning injuries during gynecologic operations. Guideline of DGGG (S1-Level, AWMF Registry No. 015/077, February 2015). Geburtsh Frauenheilk 2015; 75: 792–807
Guideline documents
The editorially complete, long version and a PDF slide set suitable for PowerPoint presentation of these guidelines as well as a summary of the conflicts of interest of all the authors can be found on the homepage of AWMF: http://www.awmf.org/leitlinien/detail/ll/015-077.html
Authors
See Table 1.
Table 1 Authors.
| AuthorMandate holder | DGGG working group/professional association/organization/society |
|---|---|
| Coordinating lead author: | |
| Prof. Dr. Markus Fleisch | German Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe [DGGG]) |
| Other lead guideline authors: | |
| Prof. Dr. Dorothee Bremerich | German Society of Anesthesiology and Surgical Intensive Care (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Anästhesiologie und operative Intensivmedizin [DGAI]) |
| Prof. Dr. Wilhelm Schulte-Mattler | German Neurological Society (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie [DGN]) |
| Dr. Antje Tannen | Expert – Institut für Gesundheits- und Pflegewissenschaft, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin |
| Prof. Dr. Dr. Alexander T. Teichmann | Consortium for Medical Law (Arbeitsgemeinschaft Medizinrecht [AG Medizinrecht]) |
| Other members of the task force: | |
| Prof. Dr. Werner Bader | Working Group Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Reconstruction (Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Urogynäkologie und plastische Beckenbodenrekonstruktion [AGUB]) |
| PD Dr. Kai Balzer | German Society for Vascular Surgery and Vascular Medicine (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Gefäßchirurgie u. Gefäßmedizin) |
| Prof. Dr. Stefan P. Renner | European Endometriosis League (Europäische Endometrioseliga [EEL]) |
| Prof. Dr. Thomas Römer | Gynecologic Endoscopy Working Group (Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Gynäkologische Endoskopie [AGE]) |
| Prof. Dr. Stephan Roth | German Urology Society (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Urologie [DGU]) |
| Prof. Dr. Florian Schütz | Gynecologic Oncology Study Group (Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Gynäkologische Onkologie [AGO]) |
| PD Dr. Marc Thill | Working Group for Plastic, Esthetic and Reconstructive Surgery in Gynecology (Arbeitsgemeinschaft Wiederherstellende Operationen in der Gynäkologie [AWOGyn]) |
| Univ.-Prof. Dr. Dr. Hans Tinneberg | German Endometriosis Research Foundation (Stiftung Endometrioseforschung [SEF]) |
| Dr. Konstantinos Zarras | German Society of Surgery (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chirurgie [DGCH]) |
Abbreviations
- AORN
Association of Perioperative Registered Nurses
- ASA
American Society of Anesthesiologists
- AST
Association of Surgical Technologists
- BGH
Bundesgerichtshof (German Federal Court of Justice)
- BMI
body mass index
- CS
compartment syndrome
- DNQP
Deutsches Netzwerk für Qualitätsentwicklung in der Pflege (German Network for Quality Development in Nursing)
- EC
epidural catheter
- EMG
electromyography
- EPUAP
European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel
- HF
high frequency
- ICP
intracompartmental pressure
- LS
lumbar spine
- MPBetreibV
Medizin-Produkte-Betreiberverordnung (German regulations governing the installation, operation and use of medical devices)
- NPUAP
National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel
- OLG
Oberlandesgericht (German Higher Regional Court)
II Using this Guideline
Purpose and objectives
The reason for preparing the guideline was the increase in requests made to advisory bodies of German medical associations to review treatments in the context of long gynecological surgeries, particularly operations where patients were placed in the lithotomy position. As recommendations on the prevention and diagnosis of injuries are sometimes contradictory, a systematic review of the existing evidence on the prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment of positioning injuries and a compilation of recommendations by a panel of experts was considered especially urgent.
Patient care
Outpatient and inpatient care.
Target audience
This guideline is addressed to the following groups of people:
-
all physicians and professionals who treat gynecological patients intra- and postoperatively, in particular:
gynecologists
anesthesiologists
nursing staff
Period of validity
The validity of this guideline was confirmed by the boards/responsible persons of the participating professional associations/working groups/organizations/societies as well as by the board of the DGGG and the DGGG Guideline Commission in February 2015 and thereby approved in its entirety. This guideline is valid from February 17, 2015 to February 28, 2018. The period of validity has been estimated based on the guidelineʼs contents. The guideline can be updated earlier if necessary; likewise, the guidelineʼs period of validity can be extended if it continues to mirror the current state of knowledge.
III Guideline
1 Methodology
The methodology for the compilation of this guideline is prescribed by the classification assigned to the guideline. The AWMF Guidance Manual and Rules for Guideline Development (Version 1.0) sets out the rules for classifying guidelines. Guidelines are differentiated into lowest (S1), moderate (S2) and highest (S3) class. The lowest class of guideline is defined as consisting of a set of recommendations for action compiled by a representative group of experts from medical societies. In 2004 the S2 class is divided into two subclasses: s2e (evidence-based) and S2k (consensus-based). The highest class (S3) combines both approaches.
This guideline is classified as: S1
In the planning stage the members of the guideline development group compiled a list of topics considered relevant for the “Prevention of Positioning Injuries during Gynecologic Operations”. A systematic literature search based on the list of topics/questions was done in PubMed using the following search terms (last updated on 31. 01. 2014): intraoperative positioning (mesh-term, n = 1582 hits), positioning damage (mesh-term, n = 672), positioning injury (mesh-term, n = 3120), intraoperative malpositioning (mesh term, n = 72), intraoperative posture (mesh term n = 1092), pressure ulcer (mesh term) AND prevention & control (subheading, n = 40) AND operation procedures (n = 47) OR perioperative prevention AND devices (n = 82), compartment syndrome (mesh term) AND postoperative (subheading) (n = 1014).
After eliminating duplicates, publications in English or German were examined with regard to their relevance for the topic. Randomized studies, case control and observational studies, case reports, reviews, meta-analyses and Cochrane reviews were included. In principle, publications were only included if they referred to types of positioning or injuries which had a particular relevance in gynecological and obstetric surgery.
Relevant recommendations and guidelines on the topic issued by the following societies were also considered:
The agreement on cooperation in gynecologic and obstetric surgery issued by the German Society of Anesthesiology and Surgical Intensive Care (DGAI) and by the Professional Association of German Anesthesiologists (Berufsverband Deutscher Anästhesisten [BDA]) together with the German Society for Gynecology and Obstetrics (DGGG) and the (German) Professional Organization of Gynecologists 1
“Recommended Practices for Positioning the Patient in the Perioperative Practice Setting” issued by the Association of Perioperative Registered Nurses (AORN): 2
“Practice Advisory for the Prevention of Perioperative Peripheral Neuropathies” of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 3 (ASA)
“AST Recommended Standards of Practice for Surgical Positioning” published by the Association of Surgical Technologists 4 (AST)
“Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: Clinical Practice Guideline” of the European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP/NPUAP) 5
The practice guidelines (Expertenstandard) issued by the German Network for Quality Development in Nursing (Deutsches Netzwerk für Qualitätsentwicklung in der Pflege [DNQP]) 6 on preventing pressure ulcers (Dekubitusprävention)
The current guideline and its synthesized recommendations for the prevention of positioning injuries were adopted by all 14 members of the Commission following an informal consensus process.
2 Preamble
Preoperative positioning of the patient and appropriate intraoperative positioning during gynecologic operations is an interdisciplinary task which requires the cooperation of professionals across a range of disciplines, all of whom have a legal obligation of due care. The aim is to ensure patient safety and prevent position-related injuries. It is also necessary to balance the surgeonʼs concerns regarding the best view of the surgical site through positioning and maneuvering the patient against the concerns of the anesthesiologist about maintaining the best and safest means of access to the patient. Moreover, the patientʼs dignity should be protected throughout the procedure.
Incorrect positioning can damage the patientʼs health; such damage can be transient but some injuries are permanent and can result in long-term functional restrictions, secondary morbidity, and even death.
Optimal patient positioning should prevent pressure injuries (pressure ulcers), skin irritation, burns, nerve damage, circulatory problems and hypothermia.
Positioning injuries can affect the skin and soft tissues, joints, ligaments and bones as well as the eyes, nerves and vessels.
3 Epidemiology
Because of muscle relaxation, patients under anesthesia lack protective reflexes and muscle tone. They are at increased risk of injury, in particular injuries such as joint luxation, plexus injuries and pressure ulcers. Moreover, around 30 % of all patients complain of back pain postoperatively, irrespective of the anesthetic technique used for the operation 7, with up to 37 % of patients complaining of back pain after undergoing surgery in the lithotomy position 8.
The overall incidence of pressure injuries reported in the literature is 5 ‰ 9. The most common patient positions used in gynecologic surgery are the supine position, various modifications of the lithotomy position 10 with or without Trendelenburg positioning, and the upright seated position (“sit-up” or “beach chair” position) for breast surgery 11. Nowadays the lithotomy position is usually modified; nevertheless it is associated with a particular risk of positioning injury. The number and duration of operations carried out with the patient in an extreme Trendelenburg position to improve exposure of the lesser pelvis in laparoscopic or robotic-assisted procedures has increased and with it the risk of positioning injuries 12, 13. The Trendelenburg position is used in these procedures to shift the abdominal viscera from the pelvis cranially to improve exposure.
Between 2008 and 2012 the advisory bodies of the regional medical associations in Germany reviewed 63 procedures in connection with charges of positioning-related injury in gynecology and obstetrics (source: German Medical Association). This corresponds to 1.8 % of all accusations of medical error in gynecology in Germany. In 31.7 % of cases the advisory bodies confirmed medical error (overall percentage for gynecology: 32 %). This percentage is higher than that of comparable procedures where there is a suspicion of positioning-related injuries during surgery in other medical specialties (22.5 %). The reviewed positioning injuries occurred almost exclusively after operations performed with the patient in a (modified) lithotomy position.
Positioning injuries during surgery are the cause of around 4 % of all medical errors confirmed by the advisory bodies of German regional medical associations, meaning that such injuries are of forensic importance.
4 Basic Forensic Aspects of Positioning
4.1 Assignment of tasks and responsibilities
The responsibility for positioning the patient preoperatively, intraoperatively and postoperatively is defined in the respective agreements of the professional societies (with the DGAI and the BDA) 1. Positioning in the operating room (OR) is divided into four stages with different persons considered responsible for correct positioning:
Preoperative stage: The anesthesiologist is responsible for positioning the patient to administer the anesthesia and for monitoring the patient until the patient is properly positioned for surgery.
Intraoperative positioning: The surgeon is responsible. The anesthesiologist must alert the surgeon if there are visible errors or concerns. The anesthesiologist is responsible for positioning of the extremities which are required to monitor the level of anesthesia and to administer anesthetics and infusions. The anesthesiologist is responsible for taking specific and appropriate precautions when positioning the patient to monitor and maintain the patientʼs vital functions.
Deliberate intraoperative change of positioning: The decision and responsibility rests with the surgeon (although the change may be initiated by the anesthesiologist). The surgeon must be alerted to unintended changes in positioning, and the surgeon must then take the decision on how to proceed and is responsible for this decision.
The anesthesiologist is responsible for positioning including repositioning of the patient after surgery up until the patient has fully recovered from the anesthesia, unless special circumstances require the involvement of the surgeon when repositioning the patient.
In all 4 stages, a qualified surgical nurse or surgical anesthesia assistant can be directed to do the actual positioning of the patient. However, at every stage, the responsibility still lies with the physician, even if the person doing the positioning is a qualified specialist for patient positioning. The qualified positioning specialist is responsible for positioning the patient properly but cannot be held liable for the decision about the position he has been directed to place the patient. A lack of general instructions regarding the type of position and a lack of monitoring of the patientʼs position is considered an organizational mistake (ruling by the German Federal Court of Justice on 24. 01. 1984 –VI ZR 203/82 – loc.cit.) 14.
The relevant agreements concluded between the respective professional associations always emphasize that a separation of responsibilities with respect to preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative positioning of patients must only be understood in the spirit of carrying out shared tasks on behalf of the patient 1. But in the event of disputes regarding liability, the precise assignment of the area of responsibility will take priority, meaning that every medical specialty and each professional group must take steps to ensure that the assigned areas of responsibility are shown clearly in the documentation. The decision about the type of position is taken based on what is required for the surgical procedure after taking the anesthesia risk into consideration 1. If the responsible anesthesiologist has concerns regarding a particular type of position because it limits monitoring or may affect the maintenance of vital functions or may be associated with a risk of positioning injury, then he must alert the surgeon to his concerns 1, 15.
In the rare case that the surgeon and the anesthesiologist cannot agree on the type of positioning, then the so-called “casting vote” principle applies, where the surgeon has the decisive vote as the primary attending physician 15. If, in such a case, the surgeon sticks to his assessment, then it must be assumed that he has done so after weighing up the competing interests 15. In this case, the surgeon bears the professional and legal responsibility for ensuring that “surgical reasons justify the increased risk associated with his preferred positioning …” 1.
4.2 Informing the patient
According to sec. 630d BGB (German Civil Code) the treating physician must obtain the patientʼs consent prior to carrying out medical treatment. According to sec. 630d para. 2 BGB the effectiveness of this consent is contingent on the patient having been informed before giving consent. Sec. 630e para. 1 BGB requires the treating physician to inform the patient of all and any circumstances relevant for consent, including in particular the nature, extent, implementation, anticipated consequences and risks involved in the treatment, unless the patient has expressly waived her right to receiving such information. The risks of positioning include pressure injuries to soft tissues, nerve lesions and compartment syndrome.
The German courts have repeatedly considered the issue of positioning injury. According to a ruling of the Higher Regional Court (Oberlandesgericht, OLG) of Cologne, the assumption that “if the patient is technically positioned correctly on the operating table, the relevant rules for positioning are complied with, and patientʼs position is monitored by the surgeon … such measures are … ‘entirely controllable’ is by no means automatic and does not apply to every type of positioning-related injury. In particular, pressure necrosis can often not be entirely avoided, even with the utmost care …” (OLG Köln, ruling on February 25, 2013, Az. 5 U 152/12, MedR 2014, 399).
One of the insights of medical science is “that despite taking the utmost care when positioning a patient, positioning injuries can nevertheless occur” (OLG Koblenz, ruling on October 22, 2009, Az. 5 U 662/08, MedR 2010, 416). Even “optimal positioning … does not always protect against developing pressure ulcers”, according to the Higher Regional Court of Hamm (OLG Hamm, ruling on May 20, 2011, Az. I-26 U 23/10).
Although the German Federal Court of Justice has stated that “the technically correct positioning of the patient on the operating table and compliance with the medical rules developed to protect patients from possible positioning injuries …” are measures which belong to the “risk area of the hospital and of the medical staff …” and which are “entirely controllable by the nursing staff and the responsible physicians”, this is not inconsistent with the physicianʼs obligation to inform the patient of the potential risk of positioning injuries. While technical methods for positioning the patient may be controllable, nevertheless, particularly in long operations, neither the positioning technique employed nor the monitoring of the patientʼs position can completely prevent a change in the patientʼs position, meaning that the positioning-related risk of neuropathies, pressure injuries, etc. cannot be completely excluded. This applies even more when patients have rare anomalies which were not detected despite complying with the current standards of care during the preliminary examination of the patient and when such anomalies facilitate pressure injuries (e.g. thoracic outlet syndrome) (BGH, ruling on January 24, 1995, NJW 1995, 1618 = VersR 1995, 539).
The fact that in medical malpractice suits the medical practitioners must provide evidence that – because it is considered controllable – technical positioning of the patient was done with the necessary care (BGH, ruling on January 24, 1995, Az. VI ZR 60/94; VersR 1995, 539) is not contrary to the obligation to inform the patient of the possible risk of positioning injuries 16, 17, because even technically perfect positioning cannot prevent pressure injury. In the above ruling of January 24, 1984, in which the BGH referred the procedure back to the appeals court for a fresh ruling, the BGH indicated that the appeals court would also have to investigate the issue “whether the consent to the operation given by the plaintiff could be invalid because of insufficient information about the risk of positioning injuries.” Accordingly, most currently available commercial information and medical history sheets include the risk of positioning injury as part of the information provided to patients 18.
4.3 Documentation
The medical practitioner bears the burden of proof in terms of showing that the patient was placed in a technically correct position, with the medical practitioner having to clear himself of the charge of malpractice in the event of positioning injury. This means that providing evidence of having proceeded appropriately and correctly is particularly important. Evidence is usually provided by registering appropriate standards which take the form of instructions on standard patient positions used in gynecology and obstetrics as well as specifically documenting the measures taken for each patient, including identifying each person who treated the patient. This documented information is generally included in preprinted form on the surgical records, which are usually collected and stored digitally and must be initialed by the person doing the positioning and the responsible physician. It is not necessary to write a detailed report on positioning the patient during surgery (BGH ruling on January 24, 1984 – VI ZR 203/82 – ArztRecht 1984, 238). Instead, if the standards have been registered, all that is required is to report and justify any individual deviations. When undertaking longer operations, it is recommended that areas likely to react sensitively to longer patient positioning times are checked and the findings documented; particularly if there is an intraoperative change of the patientʼs position, compliance with the respective standards must be recorded in the surgical report. If positioning injuries still occur, despite evidence of monitoring and readjustment of the patient position, then this is an indication that these were exceptional circumstances which, in individual cases, would qualify the assertion that the risk that occurred could have been entirely manageable.
Important forensic aspects:
Positioning is an interdisciplinary task which requires the cooperation of professionals across a range of disciplines.
Individual responsibility for positioning is divided into different stages: preoperative p. (anesthesiologist), intraoperative p. (surgeon), deliberate intraoperative change of position (surgeon), postoperative p. (anesthesiologist).
When patient-specific risk factors are present or with certain types of positioning for surgery which are considered to have an inherent risk for positioning injury (for example and primarily long operations performed with the patient in a lithotomy position), patients should be informed by their physician about risks of specific potential positioning injuries (e.g. compartment syndrome).
The standards for typical patient positions used in gynecologic interventions should be defined and recorded for every hospital and must be accessible. The staff entrusted with patient positioning (nurses, surgeons, anesthesiologists for their area of responsibility) must be trained in these standards.
Documentation of patient positions can be done with reference to the hospitalʼs recorded mandatory in-house positioning standards. Deviations from these standards must be documented. If there are no mandatory in-house standards, a detailed description of the patientʼs position and any aids used (gel mats, etc.) must be entered into the records and the surgical report.
Intraoperative monitoring by the surgeon to ensure the patient is still correctly positioned does not have to be specially documented each time; however, it is expedient to record having performed routine controls in the surgical report 15.
The patientʼs position after an intraoperative change in position (e.g. repositioning the patient from the classic lithotomy position to a flat lithotomy position) is the responsibility of the surgeon. It must be controlled and the repositioning must be documented. The extent and type of control is not specified.
5 General and Specific Aspects of Correct Positioning
General positioning recommendations for all types of positioning (“Good Practice Points”):
It is recommended that surgical units develop positioning standards, communicate them to the different medical specialties and to all professionals and staff, store the documented standards and revise them at regular intervals to ensure the contents are still up-to-date and take account of recent evidence.
Positioning materials in sufficient quantities and of a sufficient quality must be available for the operation. The type and extent of materials purchased is determined by the patient population and the state of scientific knowledge. Particularly when positioning obese patients it is important to ensure that the operating tables have the appropriate weight specification to support patients.
Co-morbidities and pre-existing conditions which are relevant for positioning must be determined preoperatively and must be taken into account when positioning the patient (AORN). These include endoprotheses and implanted devices, limited joint mobility and anatomical anomalies (insofar as these are known preoperatively).
Positioning and repositioning, if done, must be carried out by adequate numbers of personnel (AST, AORN) to ensure patient safety and the ergonomic safety of staff.
When the patient is transferred to the operating table, the patient must not be slid onto the table; the patient should be transferred using appropriate transfer devices (back boards, lifting) and with as little friction as possible to avoid injuries to the skin from shear or friction (AST).
It is important to ensure that the pad on which the patient lies is dry and crease-free (minimize the number of sheets placed under the patient).
No parts of the body should hang over the edge of the operating table; the sacrum should not extend beyond the edge of the operating table (AST, AORN).
Provide intraoperative protection against hypothermia, with active warming of the patient using warming systems (WarmTouch, Bair Huggers) where necessary.
Pad the head to ensure that the cervical spine is in a neutral position and no pressure points develop at the back of the head.
If the arms are placed in an abducted position, abduction to approx. 60° should be done with the arms in a neutral position; any further abduction requires the arms to be in a supination position. The arms should be slightly flexed at the elbow and the forearm supported by an arm supporting device. The elbow joint should be placed on a pressure-minimizing padded support, the elbow should be at least at shoulder level (AST, AORN).
Hip and knee joints should be slightly flexed, with padding of the LS where needed 7, Maximum abduction of the hips: thigh, knee and heel should be positioned to form a line to the contralateral shoulder.
Positioning of pregnant women in the second and third trimester of pregnancy: based on studies comparing maternal and fetal outcomes according to different positions during cesarean section, a Cochrane analysis came to the conclusion that there is little evidence for or against left lateral or right lateral tilt, head-up position or head-down tilt, the use of positioning wedges and cushions in the area of the LS and pelvis, and flexing or tilting the operating table 19.
In analogy to the correct positioning of pregnant women for other surgical interventions, a 15 % left lateral tilt or right lumbar positioning wedge can be used when positioning women with singleton pregnancies at the end of the second trimester and thereafter to prevent vena cava compression syndrome.
General recommendations for the lithotomy position (“Good Practice Points”):
Both leg holders must be padded and at the same height (AST, AORN).
Depending on the patientʼs physical constitution (obesity, joint mobility, etc.) the legs must be lifted into the leg holders and out of the leg holders at the end of surgery by sufficient numbers of personnel to prevent lumbosacral injury and hyperflexion of the hips (AST, AORN).
It is not known how long patients can remain in the lithotomy position without suffering positioning injury and the time probably depends on the physique and condition of the individual patient. The time spent in the lithotomy position should therefore be as short as required for the individual surgical intervention (AORN).
If the arms are placed alongside the body, it is important to watch out for the position of the fingers to prevent crush injury when moving the leg holders (AORN).
6 Prevention of Typical Positioning-related Injuries in Gynecology
Based on the available literature (observational studies) the following factors are associated with an increased incidence of positioning-related injury (Tables 2 and 3):
Table 2 Patient factors associated with a higher risk of positioning injuries.
| Patient factor | Associated risk |
|---|---|
| BMI < 20 or > 30 12 | Pressure ulcer, neuropathy |
| Diabetes mellitus 20, 21 | Neuropathy, pressure ulcer |
| Limited physical mobility (osteoarthritis, arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, knee and/or hip endoprothesis, arthrodesis etc.) | Neuropathy, pressure ulcer |
| Age > 70 years 20 | Neuropathy, pressure ulcer |
| Malnutrition 22 | Pressure ulcer |
| Peripheral arterial occlusive disease | Neuropathy |
| Smoking and COPD 12, 22, 23 | Neuropathy of the lower extremities, pressure ulcer |
| Anatomical abnormality (cervical rib, etc.) 24 | Neuropathy |
| Pre-existing neuropathies 12 | Neuropathy, pressure ulcer |
Table 3 Surgical factors associated with an increased risk of positioning injury.
| Factors specific to the type of intervention | Type of risk |
|---|---|
| “lengthy” operation (> 4 hours) 12, 25 | Pressure ulcer, neuropathy, compartment syndrome |
| Interventions performed in the lithotomy position 12 | Pressure ulcer, neuropathy, compartment syndrome |
| Interventions performed in an extreme Trendelenburg position 26 | Pressure ulcer, neuropathy, compartment syndrome |
It is recommended that patient factors and circumstances which directly affect positioning in practice (e.g. endoprothesis, arthrodesis etc.) should be noted on the surgery plan and communicated to other staff involved early on.
6.1 Positioning-related neuropathies
The overall incidence of postoperative neuropathies (including lesions caused by surgery) is reported to be 0.6–1.2 ‰ 9. However, in a study of 1210 patients who underwent major pelvic surgery the rate of postoperative neuropathies was 1.9 % 27. Neuropathies are generally caused by a combination of stretch, ischemia and pressure 28.
For practical purposes it is useful to classify the degree of severity of nerve damage into “neurapraxia”, “axonotmesis” and “neurotmesis”. This classification is important for the prognosis of nerve damage and for decisions concerning potentially necessary therapy. Neurapraxia and axonotmesis can occur in the context of positioning injury 29, 30. Neurapraxia, which represents the lowest degree of severity, results in focal blocking of impulse conduction and is limited to the affected nerve segment. It can be caused by a brief interruption of blood supply due to external compression. Regeneration can take hours, days or weeks, in rare cases even months 29, 31. Recovery after neurapraxia is complete and without sequelae. Axonotmesis is a traumatic injury with disruption of axons. The myelin sheath of Schwann cells also suffers injury but the connective tissue framework of the nerves (endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium) is preserved. After Wallerian degeneration of the axonal stump distal to the injury, the proximal axon stump forms a growth cone. The growth cone grows distally to the injury at a speed of 1 mm/day inside the preserved endoneurial sheath. If regeneration is successful, recovery of function is probable 29, 31. However, the likelihood of complete clinical recovery decreases as the distance between the nerve injury and the affected muscles increases, with increased age of the affected patient, and with increased numbers of injured axons. A nerve repair may be necessary to ensure sufficient clinical recovery (see the S3-guideline “Versorgung peripherer Nervenverletzungen” on the treatment of peripheral nerve injuries 32). Neurotmesis refers to macroscopic anatomical division of the nerves, not merely of the axons also but of all encapsulating connective tissue. Without nerve repair there will be no regeneration after neurotmesis.
6.1.1 Neuropathies of the upper extremities
Brachial plexus neuropathies: Injuries of the brachial plexus are a rare but serious complication of laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures performed with the patient in the Trendelenburg position 33, 34, 35. With an estimated incidence of 0.16 % in laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures they are reported to be the second most common nerve injury in patients under anesthesia 35, 36, 37. The plexus is at risk of injury because of its anatomical course, running from the neck, entering the intervertebral foramen to reach the axilla, passing through the scalene triangle and between the clavicle and the first rib, its proximal and distal attachment to the cervical spine and its proximity to other moving bony structures which have the potential to compress it 30, 35, 38. Compression over the acromion or of the soft tissues at 4–6 cm medial to the acromion, for example by shoulder braces, and the resulting extension of the brachial plexus in the vicinity of nerve roots C5-T1 is a major cause of positioning-related injury of the brachial plexus 28, 33, 35, 39, 40, 41. Another potential mechanism of injury is dropping of the shoulder girdle by the anesthetized and relaxed patient, resulting in the plexus becoming entrapped between the clavicle and the first rib, and hyperextension together with rotation of the cervical spine 42. Symptoms of this plexus injury include motor and sensory deficits in the shoulder, the upper arm and forearm and the hands. Anatomical variants in the patient such as the existence of a cervical rib, an abnormal course of the plexus or deformity caused by fracture are all risks predisposing to brachial plexus injury 24, 43. The prognosis for full recovery of function after such injuries is generally good, with a high probability that motor and sensory symptoms will resolve over time 44, although recovery can take several months. Nevertheless, cases with permanent functional impairment have also been described in the literature 33.
In the steep Trendelenburg position the patient is head-down in a supine position with her feet 30° higher than her head. Shoulder braces are often used to prevent the patient from sliding on the operating table 33, 45. The pressure exerted on the shoulders increases as the tilt angle in the Trendelenburg position is increased 45. The combination of arm abduction and shoulder brace appears to increase the risk of plexopathies 46. Pressure on the peripheral accessory nerve can additionally lead to trapezius muscle paresis. One study, which prospectively evaluated three different systems to prevent intraoperative sliding of the patient and simultaneously measured the pressure exerted on the shoulder with varying degrees of head-down tilt angle in non-anesthetized patients, showed that use of a medical vacuum mattress system resulted in the least pressure on the shoulders 45. Whether the use of vacuum mattresses could reduce the incidence of brachial plexus injury has not yet been demonstrated, even though many authors advocate the use of such systems. Another study compared anti-skid foam mattresses with gel pads with respect to the shifting of patients intraoperatively and found no difference between systems 47.
Recommendations for prevention (Figs. 1 to 4):
Fig. 1.
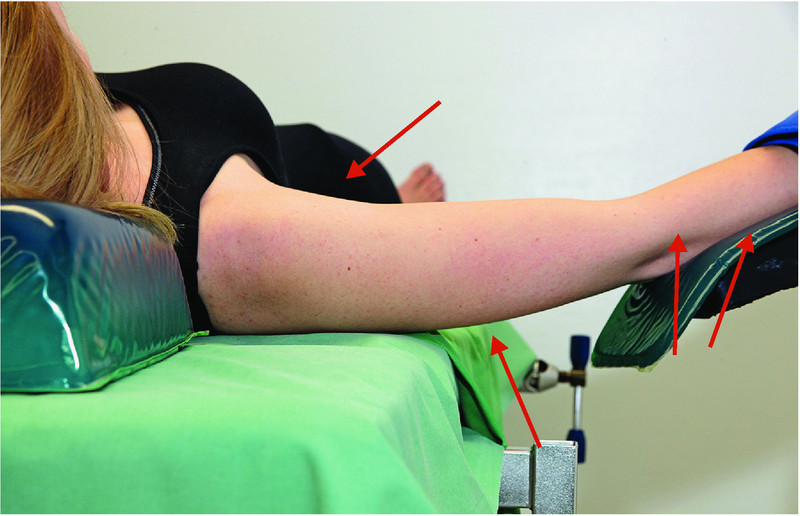
Prevention of neuropathies of the upper extremities (1): optimize positioning of the shoulder to prevent brachial plexus injury or ulnar neuropathy.
Fig. 4.
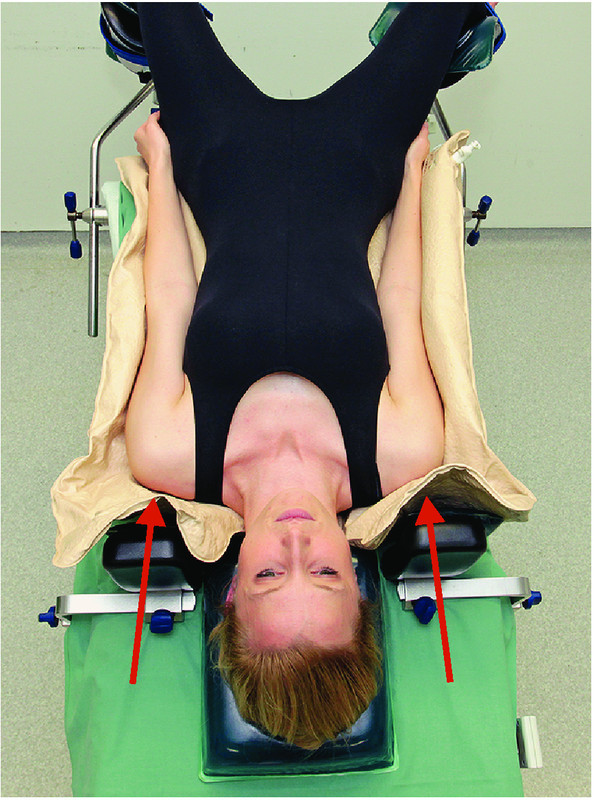
Prevention of neuropathies of the upper extremities (4): aspects of the Trendelenburg position and of the use of shoulder braces to prevent brachial plexus neuropathies.
Minimize the degree of tilt and the time spent by the patient in a head-down position after taking the surgical aspects into consideration.
Position the head using an appropriate device; avoid longer periods of hyperextension or lateral flexion/rotation; limit arm abduction to less than 90° (AORN, ASA) 28.
Arm braces must be positioned in such way that dropping of the shoulder is prevented 28.
Intraoperative sliding on the operating table should be avoided (AORN); combined with shoulder braces, the use of non-sliding operating table pads or mattresses decreases the pressure applied to the plexus. This combination should be used in preference to shoulder braces alone.
If shoulder braces are used, they must be padded and the point of contact should be at the level of the acromioclavicular joints (AORN).
If shoulder braces are used, avoid or minimize additional abduction of the arms. Arm abduction must never exceed > 90° 48.
Fig. 2 a.
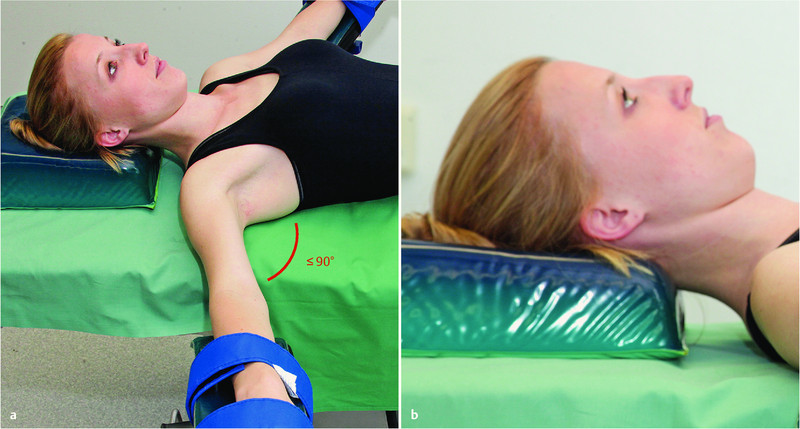
and b Prevention of neuropathies of the upper extremities (2): positioning of the head and abduction of the arm.
Fig. 3 a.
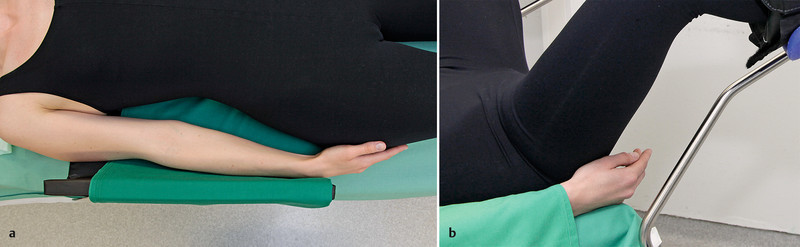
and b Prevention of neuropathies of the upper extremities (3): prevention of ulnar neuropathy and finger injuries.
Ulnar neuropathy: Because of its largely unprotected course in the ulnar nerve sulcus, the ulnar nerve is at risk of pressure injury 49. A prospective study of 1502 patients reported an incidence of 0.5 % 50. Analysis showed, however, that the risk population consisted primarily of men. This circumstance along with the fact that clinical symptoms only occurred between two and seven days after surgery suggests that factors other than inadequate patient positioning may play a role.
Clinical symptoms of injury include paresthesia of the fourth and fifth finger and on the ulnar side of the hand. The full clinical picture with involvement of ulnar nerve motor fibers results in the so-called ulnar claw 30. Pressure injuries can occur through direct pressure in the area of the elbow created by incorrect positioning of the arm, non-physiological pressure placed on the arm by the surgeon leaning on the patient, or pronation of the arm on the arm braces 30. Typical findings on neurography consist of partial conduction block without accompanying conduction delay with and without axonal injury (depending on the duration and severity of the pressure injury) or loss of motor units on electromyography (EMG). Depending on the severity (neurapraxia or axonotmesis), remission of paresis can take up to one year 51, 52.
6.1.2 Neuropathies of the lower extremity
According to a retrospective analysis of patients treated at the Mayo Clinic (Rochester/USA), persistent (≥ 6 months) motor neuropathies of the lower extremity occurred in around 1 of 3600 procedures in the lithotomy position 12. In this study, every hour the patient remained in the lithotomy position increased the risk for neuropathy by a factor of 100. In 78 % of cases the peroneal nerve was affected; the sciatic nerve was affected in 15 % of cases and the femoral nerve in 7 %. Sensory neuropathies occurred in 15 : 1000 cases 12, 13. Complete regeneration within the space of one year occurred in less than half (43 %) of all cases 12. On multivariate analysis, risk factors included BMI of 20 or less, a history of smoking within 30 days prior to the procedure, and prolonged duration of lithotomy of 4 hours or more.
Peroneal neuropathy: The common peroneal nerve, a division of the sciatic nerve, crosses the knee joint at the lateral aspect of the fibular neck 30 and divides into two branches. The superficial peroneal nerve provides sensory information but also innervates the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles required for pronation of the foot. The deep peroneal nerve innervates the muscles required to lift the foot at the ankle and the arch of the foot and provides sensory information for the web space between the first and second toe. Because of the limited soft tissue cushioning at the fibular neck there is a risk of direct pressure injury. Pressure is often caused by unpadded contact with the leg holder. Alternatively, a combination of hip flexion and knee extension can lead to non-physiological traction of the sciatic nerve and the peroneal nerves 53. Postoperative symptoms of common peroneal neuropathy include sensory deficits in the lateral lower leg and of the arch of the foot. Injury can result in motor deficits affecting the dorsal flexion of the foot, which may present clinically as drop foot. The differential diagnosis should include peroneal/sciatic injury and injury of a branch of the lumbosacral plexus which can occur in the lithotomy position 14. Low BMI, smoking and prolonged duration of intervention increase the risk 12.
Recommendations for prevention (Figs. 5 to 7):
Fig. 5.
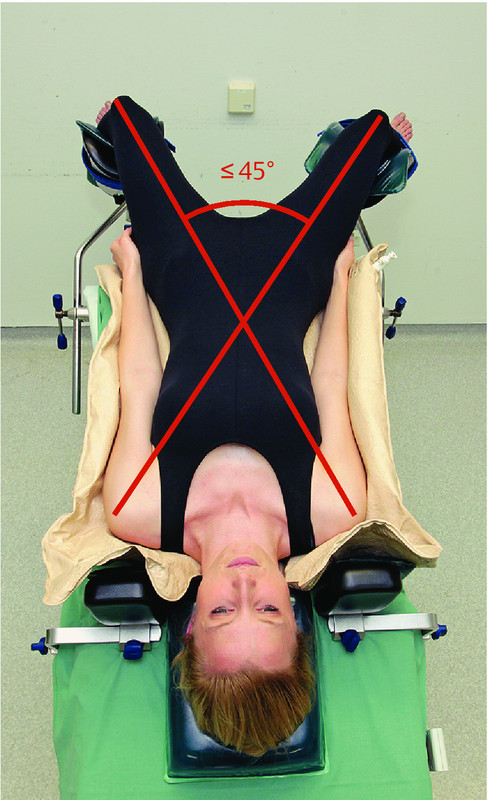
Prevention of neuropathies of the lower extremity (1): ensure correct leg abduction to prevent traction of the obturator nerve.
Fig. 7.
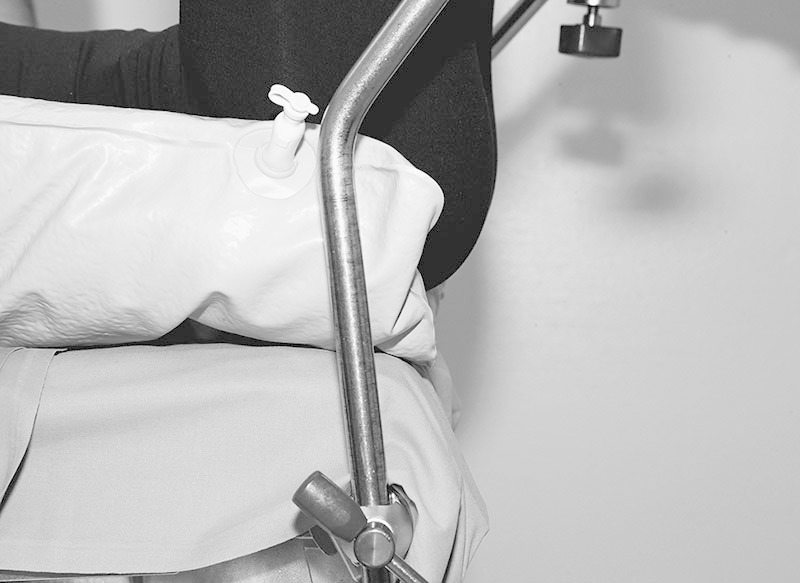
Prevention of neuropathies of the lower extremity (3): ensure optimal positioning of the sacrum in the lithotomy position.
Avoid direct pressure on the peroneal neck; pad potential pressure points.
When using stirrups with straps, the leg should not be in contact with the rods of the support (AORN).
Sciatic neuropathy: Sciatic neuropathies have been described after the patient was in a lithotomy position and after cesarean section 54, 55. The lithotomy position can result in overextension of the peroneal aspect of the sciatic nerve 53, 56, 57. Sciatic nerve lesions can lead to paresis below the knee. If knee flexion is preserved, the nerve is largely intact 58. Injury can also lead to hypesthesia in the lateral aspect of the calf and across the entire area of the foot with the exception of the inner side of the foot.
Recommendations for prevention (Figs. 5 to 7):
Avoid overextension of the ischiocrural musculature; hip flexion should not exceed > 90° 3.
Femoral neuropathy: Several gynecologic case studies have reported on femoral neuropathies after procedures in the lithotomy position 59, some of them caused by self-retaining retractor systems 60. In each case, hip abduction and extreme hip flexion with external rotation were cited as increasing the risk of injury 61, 62, 63, 64, 65. Such positioning results in mechanical bending of the femoral nerve which is pressed against the inguinal ligament. In vaginal procedures with the patient in the lithotomy position, this mechanism may even be intensified by the surgical assistant leaning against the inner aspect of the thigh 28. Clinical symptoms of femoral neuropathy include postoperative deficits in hip flexion and knee extension in combination with a reduction of the patellar reflex. The use of split leg tables, where the legs are in a supine position with abduction of both hips, is associated with femoral neuropathy. In robotic-assisted procedures where abduction was 25° the incidence for this complication was reported to be 1.7 % 66. Common symptoms are numbness of the legs and a tendency to fall when walking. Most sensory deficits disappear within five days 67. In one case study, 94 % of patients with motor symptoms experienced complete remission within 10 weeks; the remaining patients experienced remission within four months 68.
Recommendations for prevention (Figs. 6 to 8):
Fig. 6.
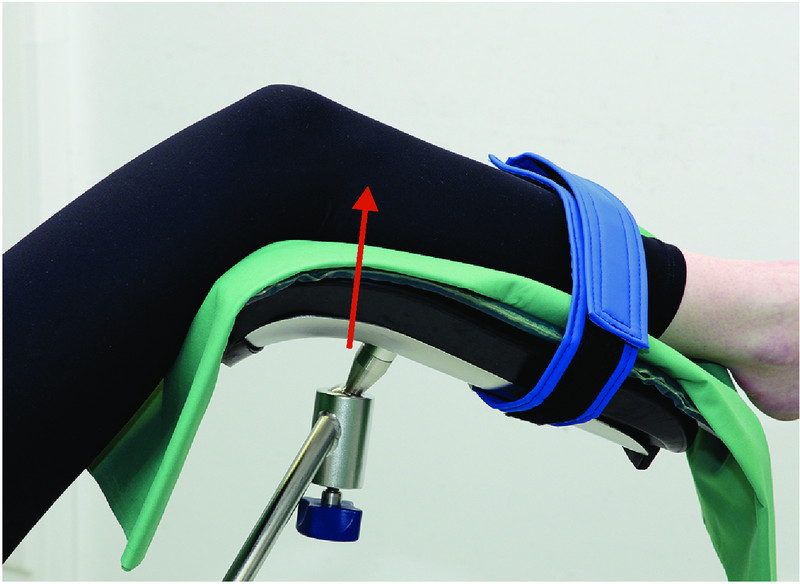
Prevention of neuropathies of the lower extremity (2): place the lower leg in padded stirrups.
Fig. 8.
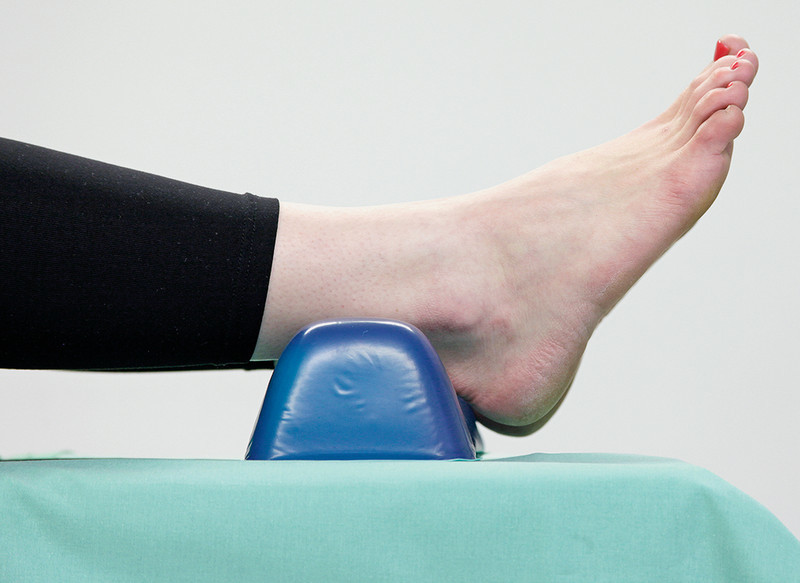
Aspects of pressure ulcer prevention.
Avoid hip flexion of > 90° in the lithotomy position; otherwise limit the time in this position.
Avoid extreme abduction and external rotation of the hip.
The surgical assistant must not lean against the inner aspect of the patientʼs thigh (AORN).
Obturator neuropathy: The obturator nerve is a nerve of the lumbar plexus. There are few reports on obturator neuropathy after procedures in the lithotomy position 69. Experiments have shown that abduction of the thigh between 30–45° in the hip joint results in significant traction of the obturator nerve which can be compensated for by hip flexion 70. Obturator nerve injury caused by pressure of the fetus on the internal pelvic wall have been described after vaginal delivery 71. This phenomenon must also be considered in the differential diagnosis of putative positioning-related obturator neuropathy after cesarean section.
Recommendations for prevention (Figs. 5 to 7):
Abduction of the lower extremity of > 30° (lithotomy position or split-leg table) must be combined with flexion of the hip to prevent positioning-related neuropathy of the obturator nerve. The abduction angle should not exceed 45°.
6.2 Postoperative non positioning-related neuropathies
Occasionally (epidemiological data are lacking), peripheral neuropathies may develop after surgery where the anatomical pathology cannot be easily explained by the procedure. Such neuropathies are usually painful or start with the patient experiencing pain followed by paresis.
Such neuropathies correspond to the clinical picture known as neuralgic shoulder amyotrophy or plexus neuritis. Neither the losses in sensory perception, which are often minimal, nor the paresis can be explained by perioperative mechanical factors affecting the peripheral nerves such as traction, pressure, or sharp dissection. In many of these patients infection is considered the cause 72, although it remains entirely unclear how surgery is a causal factor for the infection. It is not possible to give evidence-based causal recommendations for treatment, although there are reports on the use of immunoglobulins and steroids. The neurological complaints generally improve over time, but complete remission is rare. It is clear that differentiating between these postoperative inflammatory neuropathies and the above-described neuropathies caused by mechanical factors is extremely important, both clinically and forensically.
6.3 Injuries caused by high-frequency surgery
High-frequency surgery is used in most gynecological procedures for cutting or coagulation. High-frequency alternating current flows from the active electrode through conductive tissue to a larger passive electrode (neutral electrode) which conducts the current back to the high-frequency unit again, thereby closing the electric circuit. Thermal energy is created at the point of contact between the active electrode and the tissue, which creates the desired cutting or coagulation effect. Technical or operating mistakes and surgery- or patient-related factors (e.g. uncontrolled loss of bodily fluids, amniotic fluid, etc.) can potentially endanger both patient and user. If the current density under the neutral electrode is too high at any point, this can lead to the unintentional release of thermal energy 14, which can spread unnoticed from the neutral electrode. Burns mainly occur with single-surface electrodes where it is not possible to monitor the quality of the contact between electrode and patient. Liquid bridges or a point of contact between the patientʼs body and conductive material can result in leakage current. No high-frequency generator can measure and thereby avoid such leakage current. The Medizin-Produkte-Betreiberverordnung (German regulations governing the installation, operation and use of medical devices, MPBetreibV) stipulates that every user must be trained in the proper operation of and the risks associated with high-frequency units.
Prior to every application, the material used must be checked for defects.
Suspicious skin lesions which are noted postoperatively are not necessarily always associated with high-frequency current as they can also be caused by heat, pressure, time, chemicals and/or moisture (s. paragraph 6.4).
Recommendations for prevention:
The patient must be placed on a dry, insulated support; wet sheets and underlays must be replaced by dry ones.
The patient must not be in contact with electrically conductive surfaces.
Avoid any puddles of disinfectants because of the risk they may be ignited by sparks (HF surgery).
The full-sized neutral electrode should be placed near the surgical site preoperatively while maintaining sterility.
The entire surface of the neutral electrode should be in contact with the patientʼs skin; shave hairy areas if necessary.
Ensure there are no traces of liquids between the skin and the electrode; do not use additional gel.
Ensure that urine will be drained if the patient is scheduled for a lengthy surgical intervention (> 3 hours).
The use of two HF units with two separate neutral electrodes in parallel is not recommended because of the potential that power output will briefly spike, creating a higher risk of burns for the patient.
Remove all jewelry preoperatively; if an item cannot be removed, cover it with insulating tape and ensure that there is no contact with HF current and no high-frequency current is applied in the immediate vicinity of the area with the jewelry.
There must be no item of jewelry in the area between the active and the neutral electrode.
6.4 Positioning-related pressure ulcers
Pressure ulcers are undesirable complications of surgical procedures which could, in principle, be avoided. They are the cause of additional suffering for affected patients (pain), increase the time spent in hospital, and involve additional treatment costs (for materials and personnel to treat the injury).
In 2009, the European and US Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panels published a guideline on pressure ulcer prevention which included a generally accepted definition of pressure ulcers:
“A pressure ulcer is a localized injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence, as a result of pressure or pressure in combination with shear.” (European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel [EPUAP] and National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel [NPUAP], 2009).
Clear evidence of the causes of the skin injury is an essential part of the definite diagnosis (also to differentiate it from other skin injuries).
Pressure ulcers often develop in underlying tissue (just above the bony prominences in the musculature) while the overlying tissue layer initially remains intact. The injury may only become visible several days after it began to develop (i.e. during surgery).
6.4.1 Risk factors for the development of pressure ulcers
In addition to the causes of pressure ulcer described in the above definition (pressure and shear) other risk factors are also often discussed; however, their significance is not yet clear. More than 100 risk factors have been discussed in the literature 73. Risk factors proposed as potentially causative in the perioperative period include: diabetes mellitus (OR = 2.15 [1.62–2.84]) 21, duration of anesthesia and total duration of hypotonia (< 50 mmHg diastolic blood pressure) 74, age > 71 years, dehydration, excessive skin moisture, nutritional deficiencies, sensory perception disorders, lung disease 22, central or peripheral nerve block (perioperative analgesia) 75, hypothermia 76, hypotonia, vascular disease, smoking, COPD 23, patient position during surgery (a lateral position is associated with a higher risk than a supine position, OR = 8.1) and duration of surgery (OR 3.7 for every doubling in the length of surgery) 25.
The methodological quality of the studies seeking to uncover (causal) connections between the risk factors listed above and the incidence of pressure ulcers is very heterogeneous and the overall level of evidence is rather weak. There are very few studies of patient populations in a gynecological surgery setting.
6.4.2 Perioperative prevention
Risk assessment: There is some disagreement as to whether a structured risk assessment approach is absolutely necessary for the effective prevention of pressure ulcers. The instruments employed in the assessment can yield false-positive or false-negative results, and there are certain situations (such as lengthy gynecological operations) in which every patient must be treated as a potential high-risk patient. Anesthesia-induced immobility and certain positions (sitting up, lateral position) increase the pressure in the tissue at risk.
A Cochrane review of recent studies on the use of pressure ulcer risk scales to reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers showed no benefits from the use of such scales 77.
Pressure-relieving devices: The choice of device depends on the functional deficits of the patient, i.e. the extent of pressure or shear exerted on the specific body part. Depending on the extent and duration of tissue pressure, pressure on affected areas must be relieved through positioning the patient on a soft mattress to prevent/minimize cell damage. The frequency of repositioning will depend on the support surface and the overlay (EPUAP/NPUAP) 5.
A recent Cochrane review 78 analyzed studies on the efficacy of pressure-relieving devices (mattresses and overlays) and came to the result that the use of pressure-relieving overlays during surgery reduced the postoperative incidence of pressure ulcers, although two studies reported adverse skin reactions after the use of foam mattresses or overlays.
A meta-analysis 79 confirmed the protective effect of pressure-relieving mattresses compared to standard mattresses, of high-specification foam mattresses compared to standard mattresses and of certain air-filled or foam overlays compared to standard mattresses with regard to the incidence of heel pressure ulcers. A detailed health technology assessment 80 and a careful systematic review 81 confirmed the efficacy of pressure-relieving overlays used on operating tables.
The superiority of these devices compared to standard care is evident. However, comparisons between different modes of action (devices) are lacking. Obese patients represent a separate patient cohort.
Positioning: The larger the area of the body being supported, the less pressure will be placed on tissue. In heel offloading, it is important to ensure that the heels are not elevated too high because this will increase pressure on the sacral area. The same applies if the head plate is too high. The operating table should be bent with the hip in a physiologically correct position. It is important to ensure the patient does not “slide down” (e.g. by placing a rolled towel under the buttocks) because sliding not only creates pressure but may also result in shearing.
Placing the heels on a soft underlay does not appear to be as effective as heel offloading, as a soft underlay will not necessarily prevent strong pressure being exerted on underlying deep tissue.
Other positioning options include 30° oblique position, 135° angle sitting position, inclined position, etc. A systematic review showed that repositioning intervals could be reduced from every 2 hours to every 4 hours if a suitable pressure distribution device was used 82.
Other measures: According to a recent Cochrane review 83 the data from randomized controlled studies (RCTs) on the efficacy of prophylactic dressings (e.g. foam dressings or self-adhesive hydropolymer dressings to relieve pressure) to reduce the incidence of pressure ulcers (e.g. on the heels) is still too limited to allow any recommendations to be made.
The training of personnel as a supportive measure is often also studied and is recommended.
Innovative techniques such as pressure measurement or the measurement of tissue perfusion at specific body sites (sacrum) are being evaluated in preclinical trials or in the form of additional monitoring which is compared to pressure-relieving devices. The efficacy (i.e., in reducing the incidence of pressure ulcers) of regular monitoring (with an alarm) in clinical practice has not yet been studied.
Recommendations for prevention (Fig. 8):
Standardized risk assessments are not recommended.
All patients should be treated as though they are at risk.
The use of pressure-relieving overlays on operating tables is recommended.
Ensure that the largest possible area of the patient is being supported.
The prophylactic use of dressings (such as hydrocolloid dressing) to relieve pressure on healthy skin at specific sites at risk (over bony prominences) is not currently recommended.
6.5 Compartment syndrome
Acute compartment syndrome (CS) of the lower extremity is a particularly serious if rare form of positioning injury which has been almost exclusively described after lengthy operations with the patient in the lithotomy position 26, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88. CS refers to the resulting muscular and neuronal damage due to pathological increase in pressure within a confined inelastic space, in this case in one or more of the four muscular compartments of the lower leg 26, 89. If the diagnosis and start of treatment is delayed, consequences can be serious and may range from loss of function to amputation of the affected extremity and even the death of the patient from multi-organ failure. The reported incidence for gynecological procedures with the patient in the lithotomy position is reported to be between 0.028 and 0.28 % depending on the patient cohort, although the estimated number due to diagnostic error and lack of attention appears to be higher 84, 90, 91. This complication carries a high forensic relevance as treatment error is assumed to be causative in more than 50 % of cases (Source: advisory body of the North Rhine Medical Association).
The precise etiology is unclear; however decreased perfusion pressure coupled with increased pressure on the tissue (caused by resting the calf on the support) appears to result in inadequate oxygen supply to tissues. This creates ischemia which in turn leads to a further increase in tissue pressure through the activation and release of mediators and toxic metabolic products and fluid leakage from vessels. If this vicious circle is not interrupted by fasciotomy to relieve the pressure, necrosis of affected structures can follow. Numerous experiments have shown that perfusion pressure drops significantly if the leg is positioned above the right atrium or the patient is placed in the Trendelenburg position 92. An extreme lithotomy position reduces the median arterial pressure in the lower extremity to values which correspond to those measured for manifest CS, with this effect being reinforced in the Trendelenburg position 90, 93, 94. These results suggest that minimizing the time during surgery in which the patient is placed either in a lithotomy or a Trendelenburg position is the best way of preventing CS. CS has been described after using a number of very different leg supports. Although the use of slings results in a lower application of pressure on the lower leg compared to other systems 92, routine use of slings is not recommended because of the associated higher rates of other neuropathies, particularly of peroneal neuropathies 95.
The diagnosis of CS is based on clinical examination. The first signs are usually pain at some distance from the surgical site (e.g. the leg) and diminished sensation and paresthesia in the affected area 96. If an epidural catheter (EC) has been placed, the above-listed symptoms should not be exclusively ascribed to the EC; it is important to consider the possibility of incipient CS. One review found no delay in diagnosis despite postoperative analgesia if patients were adequately monitored 97.
To verify or exclude the possibility that sensory deficits and paresthesias are caused by analgesia administered in the vicinity of the spinal cord (e.g. EC), the anesthesiologist must be informed and consulted immediately. For the differential diagnosis it is useful to discontinue administration of the local analgesic through the catheter to check whether this is then followed by a drop in sensory and/or motor deficits.
Invasive measurement of intracompartmental pressure (ICP) provides additional information in cases where the constellations of symptoms is unclear, although the routine use of invasive measurement techniques is not indicated. The ICP threshold which indicates manifest CS is still controversially discussed in the literature 98. The use of pulse oximeters to monitor pressure in the extremities offers no benefits as arterial perfusion and oxygen saturation of the extremities only drop at a very late stage 99.
To date, there are no evidence-based recommendations for prevention as none of the measures proposed in the literature have been validated in prospective studies. In a prospective observational study, a drop in the incidence of CS from 0.8 to 0 % was reported for a patient cohort at high risk of CS scheduled for extensive endometriosis surgery after implementing a combination of different measures 100. These included minimizing the number of procedures performed with patients in the lithotomy position in favor of a modified supine position with the legs abducted, intermittent repositioning of the legs during surgery, and the use of vacuum mattresses to prevent the patient from slipping. The routine use of intermittent compression devices (mainly used in Anglo-American countries) has also been recommended; however other studies have reported an increased risk of complications associated with the use of these compression stockings.
Treatment of manifest CS consists of fasciotomy of all affected muscle compartments.
Recommendations for prevention:
The time which the patient spends in the lithotomy position must be kept to a minimum (AST, AORN), particularly if access to the perineum or the vagina is not required. Use of other potential alternatives such as placing the legs flat at an abduction of ≤ 45° together with slight flexion of the hip should be considered.
Where possible, the legs should be positioned at the level of or below the right atrium.
The time spent by the patient in the Trendelenburg position should also be kept to a minimum; the patient should be moved from the Trendelenburg position and repositioned as soon as it is surgically possible.
Sliding of the patient in a cranial direction must be avoided using suitable positioning aids. None of the routinely used positioning devices (gel mat vs. vacuum mattress vs. foam underlay) have been shown to be superior to any of the alternatives.
The use of typical knee-and-lower-leg leg holders should be avoided. If such leg holders are used, additional padding with gel mats is necessary.
All medical professionals involved in the perioperative care and treatment of the patient must be aware of the possibility for CS and be familiar with the clinical signs of postoperative CS after lengthy operations performed with the patient in the lithotomy position.
Routine intraoperative measurement of the compartmental pressure for early diagnosis is not recommended because of the difficulty in defining the threshold values. Invasive pressure monitoring should be additionally performed for diagnosis if symptoms are unclear and there is a clinical suspicion.
Physiological rationale suggests that intermittent repositioning of the legs in operations of 3 hours can reduce intracompartmental pressure. There is currently no evidence that this will reduce compartmental pressure in the long term or prevent CS. Neither the repositioning intervals not the appropriate duration of repositioning done intraoperatively have been validated in studies. Moreover, there is a potential risk that secondary positioning mistakes can occur due to unnoticed changes to the original (correct) position of the leg.
If the patient is additionally receiving analgesia administered in the vicinity of the spinal cord (e.g. epidural catheter), the anesthesiologist must be informed immediately. The anesthesiologist must make the differential diagnosis, identifying the causes of sensory and/or motor deficits and/or detecting a compartment syndrome where present.
7 Clinical Monitoring and Diagnosis of Positioning-related Injury
7.1 Intraoperative monitoring
Intraoperative monitoring is, by and large, unsuitable for detecting manifest positioning injury. In particular, neuropathies cannot be diagnosed in anesthetized patients.
Instead, the main tasks of intraoperative monitoring are:
controlling the patientʼs position after planned repositioning; documenting the repositioning and its control; if leg holders and arm holder are used prior to repositioning the legs, ensuring that the patientʼs fingers and hands do not get trapped or pinched;
excluding unintentional critical changes to the (presumably) correct initial position of the patient.
Other than the recommendation that the patientʼs position should be checked after planned repositioning, the start and the duration of the intervals for monitoring the patientʼs position have not been defined.
The AORN guideline has suggested considering whether patients should be repositioned intraoperatively during lengthy surgical procedures (> 4 hours) to reduce the risk of pressure-related injury (pressure ulcers, neuropathies, CS) but does not make suggestions about the time and intervals for repositioning 2. According to the most recent study reviews, there are no studies which show that active repositioning is effective for the prevention of positioning-related injury.
7.2 Postoperative monitoring
The likelihood of a positioning injury occurring can be minimized by carrying out various prophylactic measures described above; however, even if all possible care is taken, it is not possible to completely exclude positioning injury (s. also item 2.2) 15. If an injury occurs, it is important to recognize this as early as possible, make the appropriate diagnosis and provide suitable care and treatment 17.
The goal of postoperative clinical monitoring must therefore be to detect positioning injuries early on, to provide early treatment where possible. Detailed early examination of the patient (for example EMG) may help to exclude the presence of preexisting neuropathies, which can be of great forensic importance.
At the first postoperative visit by the physician to the patient who is now conscious and responsive, it is important to ask specifically about the following symptoms or carry out a targeted examination, particularly after procedures performed in the lithotomy position which is associated with a higher risk of injury:
reduced sensory perception and/or weakness in the extremities;
diffuse pain with no immediate association to the direct surgical trauma;
inspection of the skin on body areas at particular risk.
If there is a postoperative suspicion of neuropathy, it is important in addition to a potential positioning injury to consider other causes such as direct injury resulting from surgery; pressure injury resulting from hematoma or edema; and other previously unrecognized anatomical variants which can facilitate injury. A number of diseases such as diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, hypovitaminosis, uremia and malignant tumors are associated with a higher risk of neuropathies 20, 101, 102.
If specific symptoms are reported or findings of the detailed examination are suspicious, a neurological examination should be done promptly by another consultant for an objective assessment. In this context, physicians are referred to the S3-guideline on the care of peripheral nerve injuries: “Versorgung peripherer Nervenverletzungen” 32.
Every patient who is operated on in the lithotomy position for > 3 hours should undergo a postoperative clinical examination (pain, motor function, sensory perception, measurement of extent and scope) and laboratory examination where necessary (determination of creatine kinase levels) for CS.
Nursing staff must keep an eye on skin changes after surgical interventions, document any changes occurring and report them to the attending physician.
DGGG Guidelines Program
Editor
Leading Professional Medical Association
German Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe e. V. [DGGG])
Head Office of DGGG and Professional Societies
Hausvogteiplatz 12
10117 Berlin
info@dggg.de
President of DGGG
Prof. Dr. med. Diethelm Wallwiener
Universitätsfrauenklinik Tübingen
Calwerstraße 7
72076 Tübingen
DGGG Guidelines Representative
Prof. Dr. med. Matthias W. Beckmann
Universitätsklinikum Erlangen-Nürnberg
Frauenklinik
Universitätsstraße 21–23
91054 Erlangen
DGGG Guidelines Coordination
Dr. med. Paul Gaß, Tobias Brodkorb, Marion Gebhardt
Universitätsklinikum Erlangen-Nürnberg
Frauenklinik
Universitätsstraße 21–23
91054 Erlangen
fk-dggg-leitlinien@uk-erlangen.de
Supporting Information
German supporting information for this article
References
- 1.Vereinbarung über die Zusammenarbeit in der operativen Gynäkologie und in der Geburtshilfe der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Anästhesiologie und Intensivmedizin und des Berufsverbands Deutscher Anästhesisten mit der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe und dem Berufsverband der Frauenärzte. Frauenarzt. 1996;37:1172–1177. [Google Scholar]
- 2.AORN . Denver: AORN Inc.; 2014. Recommended Practices for positioning the Patient in the perioperative Practice Setting. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Practice advisory for the prevention of perioperative peripheral neuropathies: a report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Prevention of Perioperative Peripheral Neuropathies. Anesthesiology. 2000;92:1168–1182. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200004000-00036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.AST Recommended Standards of Practice for Surgical Positioning.Online:http://www.ast.orglast access: 01.01.2014
- 5.EPUAP/NPUAP Leitlinie Dekubitusprävention.Online:http://www%20epuab%20orglast access: 01.01.2014
- 6.DEUTSCHES NETZWERK FÜR QUALITÄTSENTWICKLUNG IN DER PFLEGE (DNQP) Expertenstandard Dekubitusprophylaxe in der Pflege. 2010.Online:http://www.dnqp.delast access: 01.01.2014
- 7.Larsen R. München, Jena: Urban und Fischer; 2006. Lagerung des Patienten zur Operation. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clarke A M, Stillwell S, Paterson M E. et al. Role of the surgical position in the development of postoperative low back pain. J Spinal Disord. 1993;6:238–241. doi: 10.1097/00002517-199306030-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cohen M M, Duncan P G, Pope W D. et al. A survey of 112,000 anaesthetics at one teaching hospital (1975–83) Can Anaesth Soc J. 1986;33:22–31. doi: 10.1007/BF03010904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frezza E E. The lithotomy versus the supine position for laparoscopic advanced surgeries: a historical review. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2005;15:140–144. doi: 10.1089/lap.2005.15.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hammond D C, Hollender H A, Bouwense C L. The sit-up position in breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:572–576. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200102000-00042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Warner M A, Martin J T, Schroeder D R. et al. Lower-extremity motor neuropathy associated with surgery performed on patients in a lithotomy position. Anesthesiology. 1994;81:6–12. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199407000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Warner M A, Warner D O, Harper C M. et al. Lower extremity neuropathies associated with lithotomy positions. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:938–942. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200010000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aschemann D. Heidelberg: Springer Medizin Verlag; 2009. OP-Lagerungen für Fachpersonal. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Weissauer W. Abgrenzung der Verantwortung für die operative Lagerung des Patienten und Haftung für Lagerungsschäden. Anaesthesist. 2002;51:166–174. doi: 10.1007/s00101-002-0283-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baur R, Schwenzer T. Der Lagerungsschaden bei Operationen – ein tatsächlich voll beherrschbares Risiko? GesR 5/2013, 272 – 276
- 17.Kienzle F, Ullrich W, Krier C. Lagerungsschäden in Anästhesie und operativer Intensivmedizin (Teil 2) Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 1997;32:72–86. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Berg D, Bauer H, Broglie M, Ulsenheimer K, Zwißler B. Berlin: Verlag S. Kramarz; 2013. medizin.recht. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cluver C Novikova N Hofmeyer G J et al. Maternal position during caesarean section for preventing maternal and neonatal complications Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20106CD007623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Warner M A, Warner M E, Martin J T. Ulnar neuropathy. Incidence, outcome, and risk factors in sedated or anesthetized patients. Anesthesiology. 1994;81:1332–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu P, He W, Chen H L. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for surgery-related pressure ulcers: a meta-analysis. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2012;39:495–499. doi: 10.1097/WON.0b013e318265222a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lindholm C, Sterner E, Romanelli M. et al. Hip fracture and pressure ulcers – the Pan-European Pressure Ulcer Study – intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors. Int Wound J. 2008;5:315–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2008.00452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Loorham-Battersby C M McGuiness W Heel damage and epidural analgesia: is there a connection? J Wound Care 2011202830, 32–34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Peterson T, Wissing H. Lagerungsschäden beim Patienten mit unbekanntem „thoracic outlet syndrome“. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 1995;30:516–518. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stevens J, Nichelson E, Linehan W M. et al. Risk factors for skin breakdown after renal and adrenal surgery. Urology. 2004;64:246–249. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2004.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bauer E C, Koch N, Janni W. et al. Compartment syndrome after gynecologic operations: evidence from case reports and reviews. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;173:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.10.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cardosi R J, Cox C S, Hoffman M S. Postoperative neuropathies after major pelvic surgery. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:240–244. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Winfree C J, Kline D G. Intraoperative positioning nerve injuries. Surg Neurol. 2005;63:5–18. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2004.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sunderland S. A classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function. Brain. 1951;74:491–516. doi: 10.1093/brain/74.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bradshaw A D, Advincula A P. Optimizing patient positioning and understanding radiofrequency energy in gynecologic surgery. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:511–520. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e3181ec17d3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kaye A H. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1991. Classification of Nerve Injuries; pp. 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- 32.AWMF S3-Leitlinie „Versorgung peripherer Nervenverletzungen“.Online:http://www.awmf.org/leitlinien/detail/ll/005-010.htmllast access: 01.01.2014
- 33.Shveiky D, Aseff J N, Iglesia C B. Brachial plexus injury after laparoscopic and robotic surgery. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:414–420. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2010.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Reich H. Laparoscopic treatment of extensive pelvic adhesions, including hydrosalpinx. J Reprod Med. 1987;32:736–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Romanowski L, Reich H, McGlynn F. et al. Brachial plexus neuropathies after advanced laparoscopic surgery. Fertil Steril. 1993;60:729–732. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)56233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cheney F W, Domino K B, Caplan R A. et al. Nerve injury associated with anesthesia: a closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology. 1999;90:1062–1069. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199904000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kretschmer T Heinen C W Antoniadis G et al. Iatrogenic nerve injuries Neurosurg Clin N Am 20092073–90.vii [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang J, Moore A E, Stringer M D. Iatrogenic upper limb nerve injuries: a systematic review. ANZ J Surg. 2011;81:227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2010.05597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Eteuati J, Hiscock R, Hastie I. et al. Brachial plexopathy in laparoscopic-assisted rectal surgery: a case series. Tech Coloproctol. 2013;17:293–297. doi: 10.1007/s10151-012-0920-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Advincula A P, Song A. The role of robotic surgery in gynecology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2007;19:331–336. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e328216f90b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jackson L, Keats A S. Mechanism of brachial plexus palsy following anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1965;26:190–194. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196503000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Britt B A, Gordon R A. Peripheral nerve injuries associated with anaesthesia. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1964;11:514–536. doi: 10.1007/BF03005094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cooper D E, Jenkins R S, Bready L. et al. The prevention of injuries of the brachial plexus secondary to malposition of the patient during surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;228:33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ben-David B, Stahl S. Prognosis of intraoperative brachial plexus injury: a review of 22 cases. Br J Anaesth. 1997;79:440–445. doi: 10.1093/bja/79.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suozzi B A, Brazell H D, OʼSullivan D M. et al. A comparison of shoulder pressure among different patient stabilization techniques. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:4780–4.78E7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.05.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Coppieters M W. Shoulder restraints as a potential cause for stretch neuropathies: biomechanical support for the impact of shoulder girdle depression and arm abduction on nerve strain. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:1351–1352. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200606000-00050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Klauschie J, Wechter M E, Jacob K. et al. Use of anti-skid material and patient-positioning to prevent patient shifting during robotic-assisted gynecologic procedures. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010;17:504–507. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2010.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mitterschiffthaler G, Theiner A, Posch G. et al. Läsion des Plexus brachialis, verursacht durch fehlerhafte Operationslagerungen. Anasth Intensivther Notfallmed. 1987;22:177–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Haupt W. Intraoperative Lagerungsschäden des Nervus ulnaris bei anatomischen Varianten. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1998;114:1789–1792. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1066830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Warner M A, Warner D O, Matsumoto J Y. et al. Ulnar neuropathy in surgical patients. Anesthesiology. 1999;90:54–59. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199901000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kastrup O. Stuttgart: Thieme; 2012. Diagnostik und Therapie der chronischen Ulnarisneuropathie am Ellenbogen (ulnarneuropathy at the elbow, UNE) [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stoelting R K. Postoperative ulnar nerve palsy–is it a preventable complication? Anesth Analg. 1993;76:7–9. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Burkhart F L, Daly J W. Sciatic and peroneal nerve injury: a complication of vaginal operations. Obstet Gynecol. 1966;28:99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Roy S, Levine A B, Herbison G J. et al. Intraoperative positioning during cesarean as a cause of sciatic neuropathy. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:652–653. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(01)01700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Umo-Etuk J, Yentis S M. Sciatic nerve injury and caesarean section. Anaesthesia. 1997;52:605–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Batres F, Barclay D L. Sciatic nerve injury during gynecologic procedures using the lithotomy position. Obstet Gynecol. 1983;62:92s–94s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.McQuarrie H G, Harris J W, Ellsworth H S. et al. Sciatic neuropathy complicating vaginal hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972;113:223–232. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90771-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Martin J. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1987. Positioning in Anaesthesia and Surgery. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dunnihoo D, Huddleston H, North S. Femoral nerve palsy as a complication of vaginal hysterectomy – review of the world literature. J Gynecol Surg. 1994;10:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chan J K, Manetta A. Prevention of femoral nerve injuries in gynecologic surgery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186:1–7. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.119182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hopper C L, Baker J B. Bilateral femoral neuropathy complicating vaginal hysterectomy. Analysis of contributing factors in 3 patients. Obstet Gynecol. 1968;32:543–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Raber G, Schneider H P. [Femoral nerve paralysis after vaginal hysterectomy and its forensic importance] Zentralbl Gynakol. 1993;115:273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.al Hakim M, Katirji B. Femoral mononeuropathy induced by the lithotomy position: a report of 5 cases with a review of literature. Muscle Nerve. 1993;16:891–895. doi: 10.1002/mus.880160902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Roblee M A. Femoral neuropathy from the lithotomy position: case report and new leg holder for prevention. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967;97:871–872. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90625-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sinclair R H, Pratt J H. Femoral neuropathy after pelvic operation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972;112:404–407. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90486-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Koc G, Tazeh N N, Joudi F N. et al. Lower extremity neuropathies after robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy on a split-leg table. J Endourol. 2012;26:1026–1029. doi: 10.1089/end.2011.0653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Warner M A. Perioperative neuropathies. Mayo Clin Proc. 1998;73:567–574. doi: 10.4065/73.6.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Goldman J A, Feldberg D, Dicker D. et al. Femoral neuropathy subsequent to abdominal hysterectomy. A comparative study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1985;20:385–392. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(85)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Glenn J. Neural damage resulting from dorsal lithotomy positioning. Surg Rounds. 1981;4:42–46. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Litwiller J P, Wells R E jr., Halliwill J R. et al. Effect of lithotomy positions on strain of the obturator and lateral femoral cutaneous nerves. Clin Anat. 2004;17:45–49. doi: 10.1002/ca.10168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lindner A, Schulte-Mattler W, Zierz S. Postpartales Nervus obturatorius-Syndrom: Fallbericht und Übersicht über die Nervenkompressionssyndrome während Schwangerschaft und Geburt. Zentralbl Gynäkol. 1997;119:93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Staff N P, Engelstad J, Klein C J. et al. Post-surgical inflammatory neuropathy. Brain. 2010;133:2866–2880. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Collier M, Moore Z. London: Springer; 2006. Pressure Ulcer Aetiology and Risk Factors; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Connor T Sledge J A Bryant-Wiersema L et al. Identification of pre-operative and intra-operative variables predictive of pressure ulcer development in patients undergoing urologic surgical procedures Urol Nurs 201030289–295.305 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Edwards J L, Pandit H, Popat M T. Perioperative analgesia: a factor in the development of heel pressure ulcers? Br J Nurs. 2006;15:S20–S25. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2006.15.Sup1.20688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Scott E M Leaper D J Clark M et al. Effects of warming therapy on pressure ulcers–a randomized trial AORN J 200173921–933.936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Moore Z E Cowman S Risk assessment tools for the prevention of pressure ulcers Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20142CD006471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.McInnes E The use of pressure-relieving devices (beds, mattresses and overlays) for the prevention of pressure ulcers in primary and secondary care J Tissue Viability 2004144–6.8–10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Nicosia G, Gliatta A E, Woodbury M G. et al. The effect of pressure-relieving surfaces on the prevention of heel ulcers in a variety of settings: a meta-analysis. Int Wound J. 2007;4:197–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2007.00333.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Cullum N, Nelson E A, Flemming K. et al. Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy. Health Technol Assess. 2001;5:1–221. doi: 10.3310/hta5090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Reddy M, Gill S S, Rochon P A. Preventing pressure ulcers: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296:974–984. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.8.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Krapfl L A, Gray M. Does regular repositioning prevent pressure ulcers? J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2008;35:571–577. doi: 10.1097/01.WON.0000341469.33567.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Moore Z E Webster J Dressings and topical agents for preventing pressure ulcers Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20138CD009362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Schofield P F, Grace R H. Acute compartment syndrome of the legs after colorectal surgery. Colorectal Dis. 2004;6:285–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2004.00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Adler L M, Loughlin J S, Morin C J. et al. Bilateral compartment syndrome after a long gynecologic operation in the lithotomy position. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;162:1271–1272. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Lawrenz B, Kraemer B, Wallwiener D. et al. Lower extremity compartment syndrome after laparoscopic radical hysterectomy: brief report of an unusual complication of laparoscopic positioning requirements. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:531–533. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2011.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Szalay G, Meyer C, Alt V. et al. Das lagerungsbedingte Kompartmentsyndrom des Unterschenkels als Komplikation nach Eingriffen in Steinschnittposition. Zentralbl Chir. 2010;135:163–167. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1224706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Tonnies P, Stogbauer R, Watermann D. et al. Unterschenkel-Kompartmentsyndrom nach langdauernden gynäkologischen Operationen in Steinschnittlage. Zentralbl Gynakol. 1999;121:149–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Matsen F A 3rd, Krugmire R B jr.. Compartmental syndromes. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978;147:943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Halliwill J R, Hewitt S A, Joyner M J. et al. Effect of various lithotomy positions on lower-extremity blood pressure. Anesthesiology. 1998;89:1373–1376. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199812000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bauer E C, Koch N, Erichsen C J. et al. Survey of compartment syndrome of the lower extremity after gynecological operations. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2014;399:343–348. doi: 10.1007/s00423-014-1172-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Martin J T. Compartment syndromes: concepts and perspectives for the anesthesiologist. Anesth Analg. 1992;75:275–283. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199208000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Horgan A F, Geddes S, Finlay I G. Lloyd-Davies position with Trendelenburg–a disaster waiting to happen? Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:916–919. doi: 10.1007/BF02237102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Svendsen L B, Flink P, Wojdemann M. et al. Muscle oxygen saturation during surgery in the lithotomy position. Clin Physiol. 1997;17:433–438. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2281.1997.04747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Leff R G, Shapiro S R. Lower extremity complications of the lithotomy position: prevention and management. J Urol. 1979;122:138–139. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Tiwari A, Haq A I, Myint F. et al. Acute compartment syndromes. Br J Surg. 2002;89:397–412. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-1323.2002.02063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mar G J, Barrington M J, McGuirk B R. Acute compartment syndrome of the lower limb and the effect of postoperative analgesia on diagnosis. Br J Anaesth. 2009;102:3–11. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Pfeffer S D, Halliwill J R, Warner M A. Effects of lithotomy position and external compression on lower leg muscle compartment pressure. Anesthesiology. 2001;95:632–636. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200109000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mars M, Hadley G P. Failure of pulse oximetry in the assessment of raised limb intracompartmental pressure. Injury. 1994;25:379–381. doi: 10.1016/0020-1383(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Tomassetti C, Meuleman C, Vanacker B. et al. Lower limb compartment syndrome as a complication of laparoscopic laser surgery for severe endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:2.038E12–2.038E15. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.07.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Wey J M, Guinn G A. Ulnar nerve injury with open-heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 1985;39:358–360. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Zylicz Z, Nuyten F J, Notermans S L. et al. Postoperative ulnar neuropathy after kidney transplantation. Anaesthesia. 1984;39:1117–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb08935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
German supporting information for this article


