Figure 1. Linoleoyl sn-2 residues of ether phosphocholines are truncated by radical oxidation.
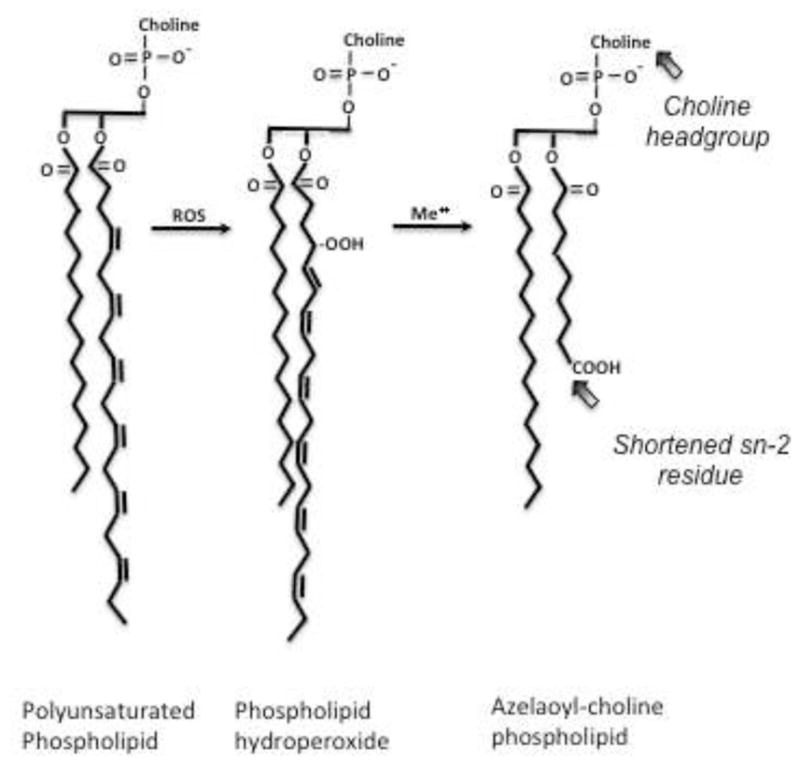
Hydrogen ion extraction between vicinal ethanolic bonds of polyunsaturated fatty acyl residues is followed by rearrangement to direct molecular oxygen incorporation at the distal and proximal end of the run of double bonds, forming phospholipid hydroperoxide (hydro)peroxides at these sites. The abundant sn-2 linoleoyl residue thereby produces nine carbon azelaoyl (nonanedioic acid) residues that remain esterified to the glyceryl phospholipid backbone. Oxidative truncation of linoleyl choline phospholipid to azelaoyl choline phospholipid generates a PAF-like agonist that stimulates the G protein coupled receptor for Platelet-activating Factor (PAF), the PTAFR. The critical elements recognized by this G protein coupled receptor include the short sn-2 acyl chain and the choline sn-3 headgroup;
