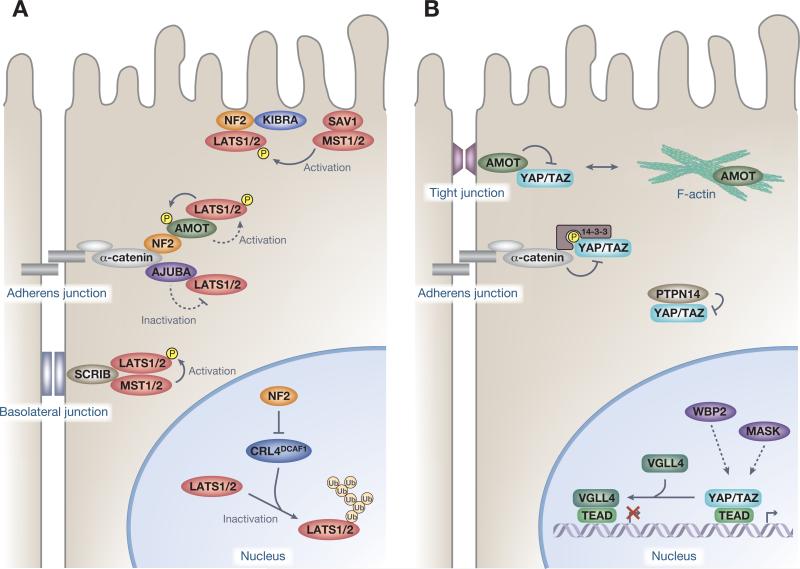
Figure 2.
Regulators of Yes-associated protein (YAP)/transcriptional coactivator with a PDZ-binding domain (TAZ) activities. (A) Spatial organization and regulation of the kinase module. Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) (also known as Merlin) activates large tumor suppressor (LATS) kinases at multiple levels. NF2 recruits LATS at the plasma membrane to coordinate the activating phosphorylation by the mammalian STE20-like protein kinase (MST)–Salvador family WW domain-containing protein 1 (SAV1) kinase complex. NF2 directly interacts with α-catenin and Angiomotin (AMOT) to recruit LATS kinases at the adherens junction, which in turn activate LATS. NF2 inhibits the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4DCAF1-mediated ubiquitylation of LATS1/2 in the nucleus to inhibit proteasomal degradation of LATS1 and ubiquitylation-induced conformational change of LATS2. Scribble (SCRIB) recruits the core kinases MST and LATS to facilitate LATS activation at the basolateral junction. LATS recruitment by AJUBA at adherens junctions inhibits LATS kinase activity. (B) Physical regulation of the transcription module. AMOT, protein tyrosine phosphatase 14 (PTPN14), and α-catenin inhibit the activity of the transcription module by complexing YAP and TAZ, thus sequestering and preventing their nuclear access. AMOT interacts with and thereby causes cytoplasmic sequestration of YAP and TAZ by recruiting them to tight junctions. PTPN14 also causes cytoplasmic localization of YAP and decreased nuclear YAP activity. The adherens junctions protein α-catenin also regulates YAP by sequestering YAP–14-3-3 protein complexes in the cytoplasm. WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2) and multiple ankyrin repeats single KH domain-containing protein (MASK) interact with nuclear YAP and TAZ, which enhances YAP and TAZ transcriptional coactivator properties, but the precise mechanism remains unknown. Vestigial-like family member 4 (VGLL4) represses target gene expression by competing with YAP–TEA domain family (TEAD) interactions.