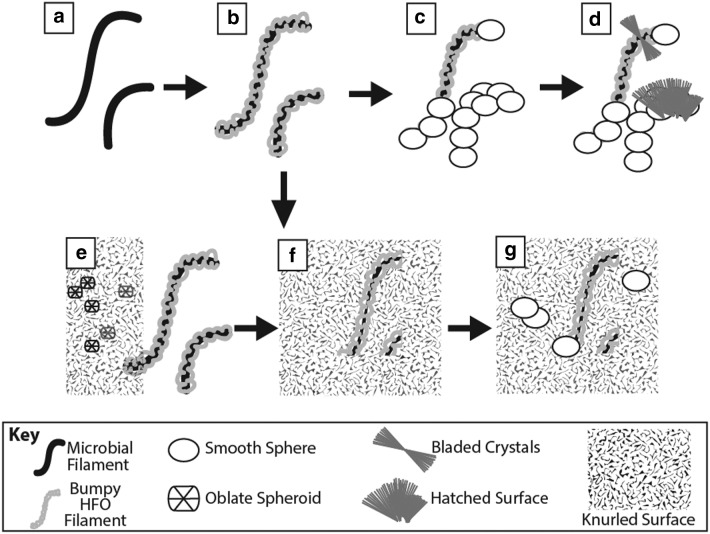
FIG. 12.
Bumpy HFO filament formation schematic in the in situ gossan. Bare microbial filaments (a) are coated with submicrometer HFO particles (b). Euhedral HFO minerals coat the filaments and fill in void space, preserving the HFO filament structures. Smooth spheres nucleated on bumpy HFO filaments (c). Bladed crystals then nucleated on surfaces, including bumpy HFO filaments, and grew together to form a hatched surface (d). Hatched surfaces grew as a front over HFO filaments and smooth spheres. In contrast to the microenvironments with smooth spheres and bladed crystals, bumpy HFO filaments are also preserved by rough oblate spheroids that grew together as knurled surfaces (e). These fronts also overgrew bumpy HFO filaments, reducing void space and preserving the filaments (f). Smooth spheres then overgrew knurled surfaces and rough oblate spheroids, further reducing void space (g).