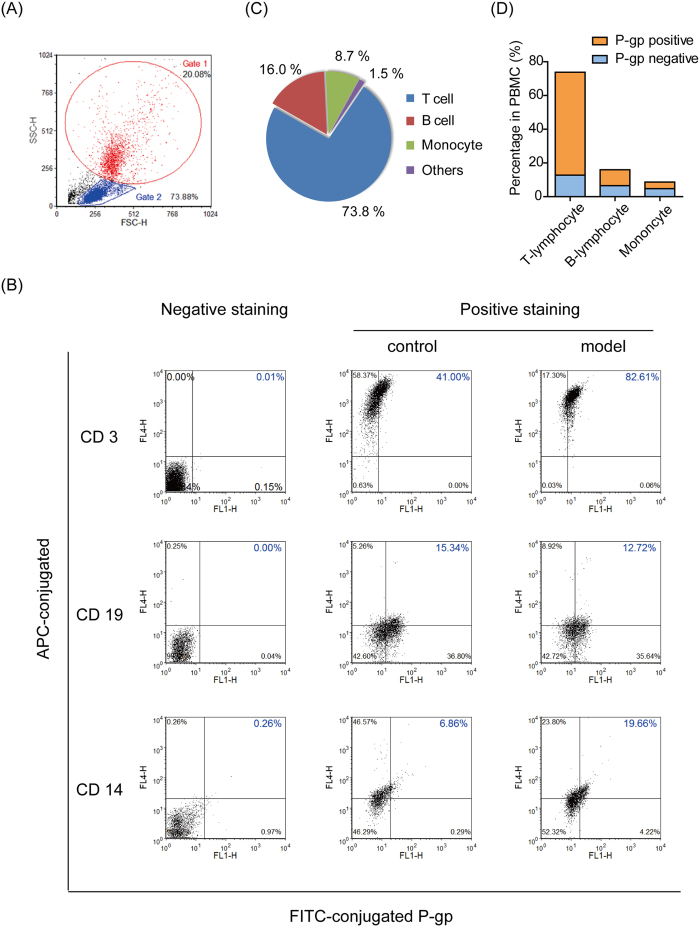
Figure 3. T-lymphocytes with high P-gp expression dominated the PBMC of TNBS-induced mice.
Isolated PBMC were incubated with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse P-gp antibody together with APC-conjugated anti-mouse CD3, CD14 or CD19 antibodies. The data were acquired on a BD FACSVerse flow cytometer and analyzed. (A) The cells were first gated crudely for monocytes (Gate1) or lymphocytes (Gate2) using SSC-H vs. FSC-H. (B) The cells in Gate1 or Gate2 were further quadrant-gated by comparing them with the negative-stained group, and FITC/APC double-positive staining (upper right in quadrant gating) was considered to represent positive P-gp expression in T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+) and monocytes (CD14+). (C) By multiplying the percentage of APC-positive (upper left and upper right quadrant gating) cells in Gate1/Gate2 by the percentage of Gate1/Gate2 in PBMC, the relative contents of T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and monocytes in the PBMC of colitis mice were determined. (D) By multiplying the percentage of FITC/APC double-positive (upper right in quadrant gating) cells in Gate1/Gate2 by the percentage of Gate1/Gate2 in PBMC, the percentages of positive P-gp expressing T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and monocytes in the PBMC of colitis mice were determined.