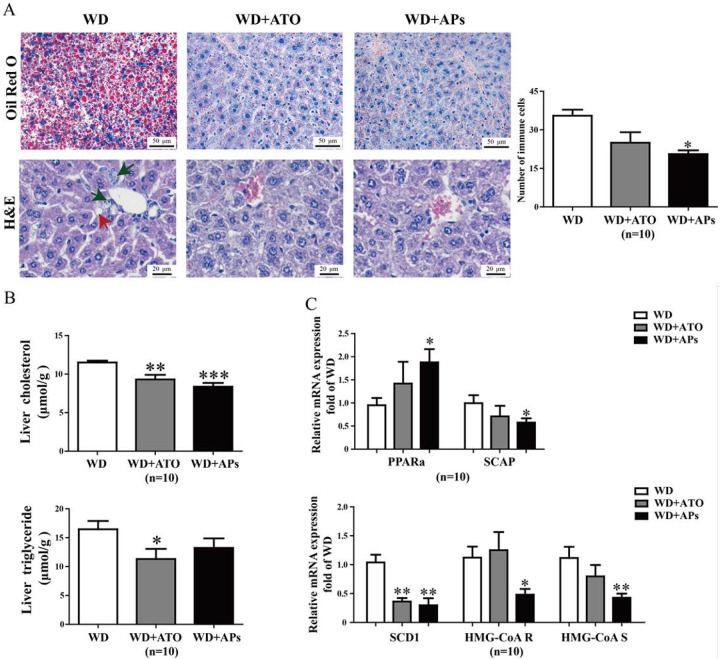
Figure 3.
The APs attenuate hepatic lipid deposition, lipogenesis and inflammatory cell infiltration in the livers of WD-fed ApoE−/− mice. A: Hepatic lipid deposition was measured in WD-fed ApoE−/− mice treated with APs (100 mg/kg/day) or ATO (10 mg/kg/day) for 12 weeks. Microscopic examination of Oil Red O and H&E stained-liver sections revealed decreased accumulation of neutral fat and steatosis in the APs- or ATO-treated mice compared to the WD model mice. The red arrow shows the steatosis in the liver, and the black arrow shows the infiltration of inflammatory cells; B: Hepatic TG and total cholesterol levels were measured in the ApoE−/− mice fed with WD, WD + ATO, or WD + Aps; C: mRNA levels of the hepatic genes—SCAP, PPARα, SCD-1, HMG-CoA R and HMG-CoA S were determined by real-time PCR. These genes are involved in lipid metabolism. The values are presented as the means ± S.E.M., n = 10 per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. WD mice.