Figure 2.
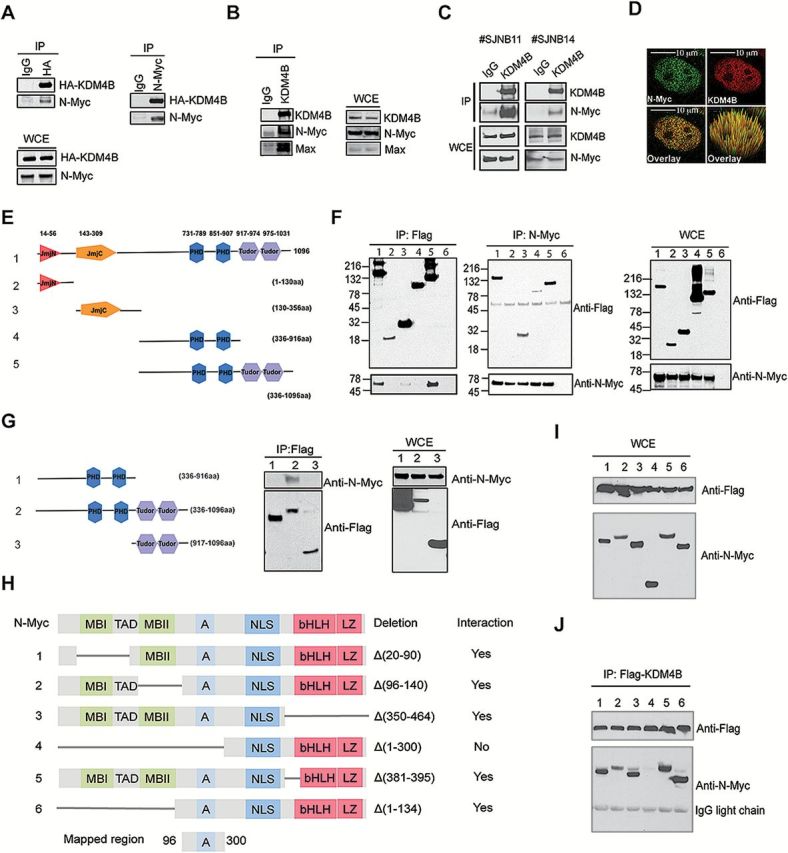
Assessment of the physical interaction of KDM4B and N-Myc. A) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation of HA-KDM4B and N-Myc overexpressed in 293T cells. 5% of total cell lysates was used as input. IP = immunoprecipitation; WCE = whole cell lysates. B) Immunoprecipitation of the endogenous KDM4B and N-Myc complex from SK-N-BE2 cells. 5% of total cell lysates was used as input. C) Immunoprecipitation of the endogenous KDM4B and N-Myc complex from human neuroblastoma xenografts. 5% of total cell lysates was used as input. D) Example of confocal immunofluorescence microscopy assessment of endogenous KDM4B and N-Myc in SK-N-BE2 cells (100X). More than 90% of the cells showed overlapping expression when 50 cells were evaluated. Scale bar = 10 µM. E) Flag-tagged constructs of different fragments of KDM4B. F) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation of flag-tagged KDM4B fragments and N-Myc overexpressed in 293T cells. Lane 6 is an IgG control. 5% of total cell lysates were used as input. G) Immunoprecipitation of flag-tagged KDM4B fragments as indicated and N-Myc overexpressed in 293T cells. 5% of total cell lysates were used as input. H) Deletion mutants of N-Myc. A = acidic central region; bHLH = basic helix-loop-helix; LZ = leucine zipper domain; MBI and MBII = MYC Box I and II; NLS = nuclear localization signal; TAD = transactivation domain. I) Input for immunoprecipitation in (J). J) Immunoprecipitation of flag-tagged KDM4B and MYCN deletion mutants as shown in (H) overexpressed in 293T cells.
