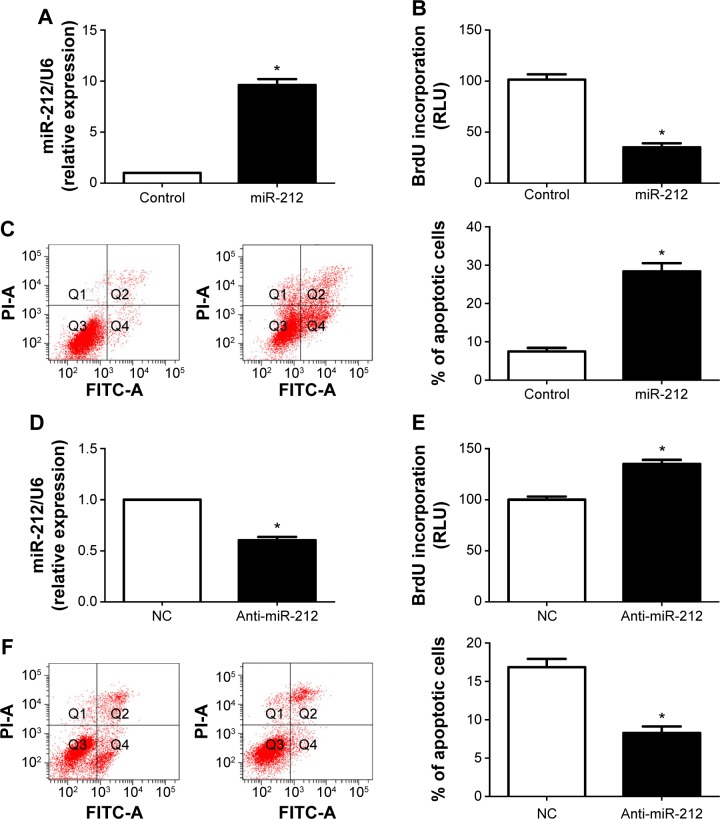
Figure 2.
miR-212 reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HCC cells.
Notes: (A) HepG2 cells that were transfected with miR-control (control) and miR-212, respectively, were subjected to qRT-PCR for miR-212 expression. n=3 independent experiments, *P<0.05. (B) Cell proliferation as measured by BrdU incorporation assays was inhibited by upregulation of miR-212 in HepG2 cells as compared with control cells. n=3 repeats with similar results, *P<0.05. (C) miR-212 overexpressing HepG2 cells conferred a larger subgroup of apoptotic cells as compared with control cells. n=3 repeats with similar results, *P<0.05. (D) Huh7 cells that were transfected with negative control (NC) and miR-212 inhibitor (anti-miR-212), respectively, were subjected to qRT-PCR for miR-212 expression. n=3 independent experiments, *P<0.05. (E and F) Downregulation of miR-212 promoted cell proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in Huh7 cells. n=3 repeats with similar results, *P<0.05.
Abbreviations: BrdU, 5-bromodeoxyuridine; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-212, microRNA 212; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; RLU, relative light unit; PI, propidium iodide.