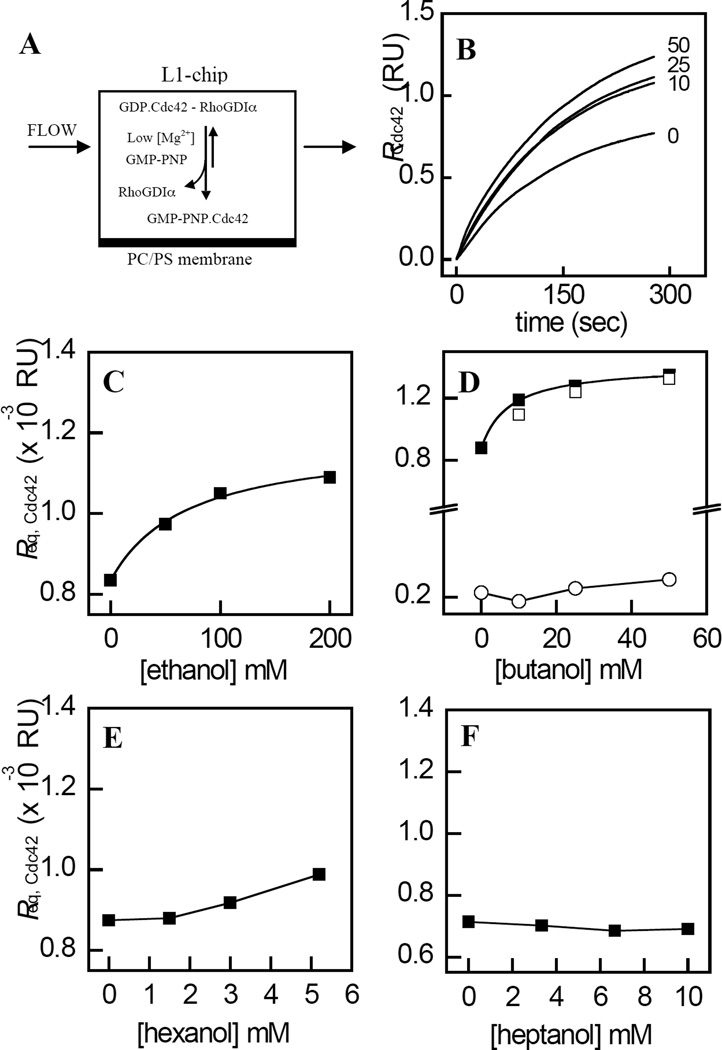
Figure 9.
Enhanced membrane-association of Cdc42 by n-alkanols resulting from the destabilization of the RhoGDIα–Cdc42 complex. A, the association of Cdc42 with POPC/POPS (4:1, molar) membranes immobilized on a Biacore L1 chip, was measured from the increase in response (binding) that occurred upon injection of the RhoGDIα– Cdc42 complex in the presence of EDTA and GMPPNP. B, representative time courses for the concentration dependent effects of n-butanol on Cdc42 membrane-association. C– F, values of Req,Cdc42, calculated from fits of the time courses obtained for each concentration of n-alkanols with chain lengths 2, 4, 6, and 7 to Eq. 5, were plotted as function of n-alkanol concentration. Also shown is the effect of n-butanol on Req,Cdc42 values obtained in the absence of EDTA and GMPPNP (Panel D , ○), and the concentration dependent effects of 3-azibutanol on Req,Cdc42 (Panel C, □). The solid curves represent fits of the data to Eq. 6 using least squares non-linear regression analysis. Values of EC50 and h are listed in Table 1. Data are representative of three independent experiments. The fits of each individual replicate experiment yielded similar parameter values and errors. Other details are described in “Experimental Procedures.”