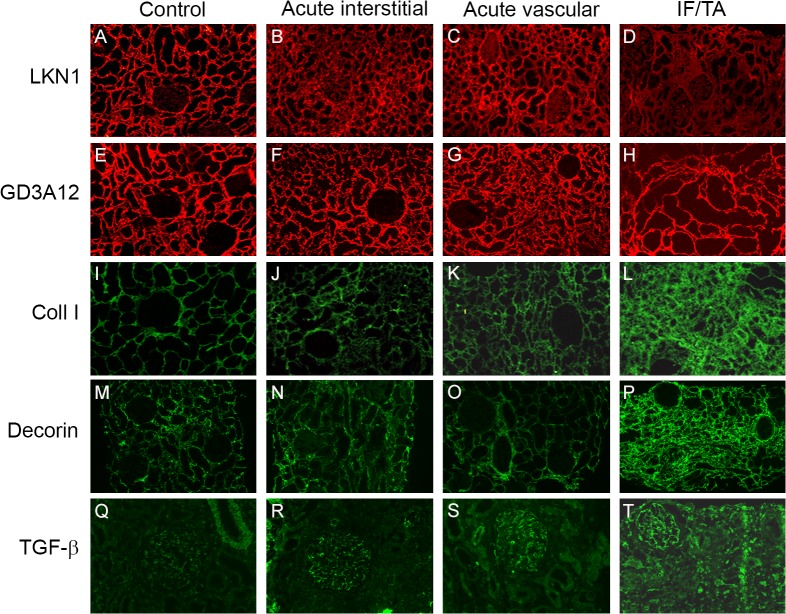
Fig 1. Expression of the 4/2,4-di-O-sulfated and IdoA-Gal-NAc4S DS domains defined by the antibodies LKN1 (A-D) and GD3A12 (E-H), type I collagen (I-L), decorin (M-P) and TGF-β (Q-T) in renal allograft rejection and controls.
Representative photographs showing the expression of the 4/2,4-di-O-sulfated DS domain defined by LKN1 in the control human kidneys (A). Tubular interstitial expression of this 4/2,4-di-O-sulfated DS domain defined by LKN1 was increased in acute interstitial (B) and acute vascular (C) renal allograft rejections compared to interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA) (D). Expression of the IdoA-Gal-NAc4S DS domain recognized by GD3A12 was similar in the control human kidney and the three types of renal allograft rejection (E-H), while expression of type I collagen (coll I) and decorin was increased in IF/TA (L, P) compared to the control human kidney (I, M), and acute interstitial (J, N) and acute vascular renal allograft rejections (K, O). Glomerular expression of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) was increased in the three types of renal allograft rejection (R-T) compared to the control human kidney (Q). Magnification A-P 100x, magnification Q-T 200x.