Figure 2. Significant differences in brain response to positively valenced faces between FH+Pain and FH−Pain youth.
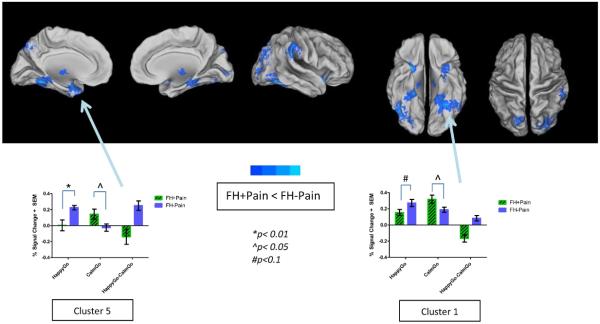
Brain response to Happy vs. Calm Go faces was reduced in FH+Pain youth compared with their FH−Pain peers, as indicated by areas in cool colors surface-mapped on the Population-Average, Landmark- and Surface-based (PALS-B12) template brain, multiple comparison corrected, (p/α<0.05/0.05). These nine clusters are labeled on the maps with names corresponding to regions where the peak coordinate of differences in brain response was located, and include occipital, parietal, frontal, thalamic, and limbic brain regions. Brain activity is bar graphed from two of these clusters (Clusters 1 and 5) as examples of patterns seen in both the contrast of Happy vs. Calm Go faces, and the simple effects of those contrasts. In both regions group differences suggest blunted activity to Happy faces, but increased activity to Calm faces in FH+Pain youth, compared with their FH−Pain peers. L = left, R = right.
