Fig. 5.
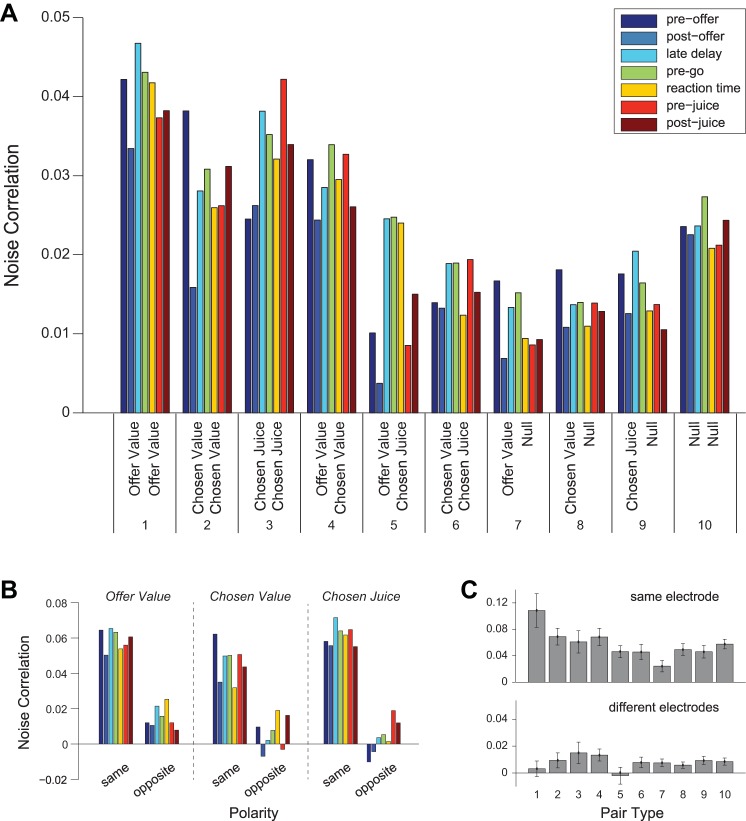
Noise correlations for different pair types. A: mean rnoise recorded for 10 pair types and 7 time windows. The no. of pairs for each pair type is indicated in Table 1, and colors indicate different time windows. Pooling time windows, rnoise varied significantly across pair type (P < 10−3, 1-way ANOVA). Post hoc tests found several significant differences in rnoise: type 1 > types 6–10, type 2 > types 7–9, type 3 > types 6–8, type 4 > types 7–9, and type 10 > types 7–8 (all P < 0.05, Tukey's least-significant difference). We also observed consistent trends across time windows. Starting from the preoffer time window (baseline), rnoise decreased in the postoffer time window. It then increased in the delay and pre-go time windows compared with the postoffer. It decreased again in the reaction time time window and remained roughly stable for the rest of the trial. These trends were observed for all pair types (with the exception of pair type 3 in the preoffer time window; see main text). B: mean rnoise for pair types 1-3, divided by juice polarity (see materials and methods). Pairs of neurons with the same polarity are on the left of each panel, while those with opposite polarities are on the right. For chosen juice pairs with opposite polarity, residual activity from the previous trial leads to negative noise correlations in the preoffer time window. C: mean rnoise by pair type. Data from different time windows are averaged separately for cell pairs recorded from the same electrode (top) and from different electrodes (bottom). All error bars indicate SE.