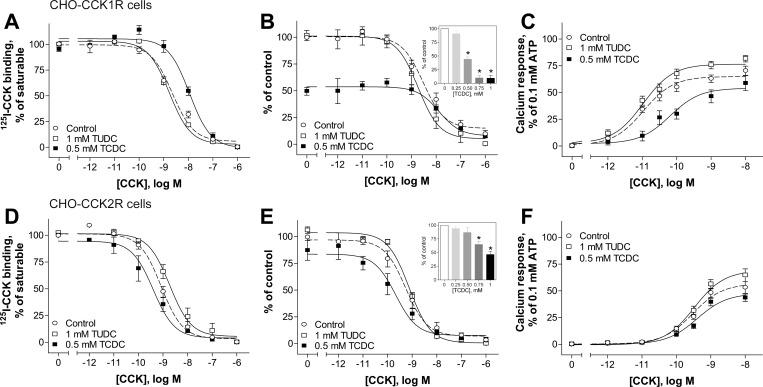
Fig. 2.
Effects of bile acids on natural ligand binding to and biological activity at the CCK receptors CCK1R and CCK2R in a normal membrane environment. A, B, D, and E: CCK competition-binding curves for Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-CCK1R (A and B) and CHO-CCK2R (D and E) cells in the absence (control) and presence of 1 mM TUDC and 0.5 mM TCDC. Insets: effects of increasing concentration of TCDC on specific CCK binding at the CCK1R (B) and CCK2R (E). Values (means ± SE of ≥3 independent experiments performed in duplicate) represent percentages of saturable binding for each curve (A and D) or percentage of control (B and E). C and F: typical concentration-dependent curves for intracellular calcium responses to CCK in CHO cells stably expressing CCK1R (C) and CCK2R (F) in the absence and presence of bile acids. Values (means ± SE of ≥8 independent experiments performed in duplicate) were normalized to maximal response to 0.1 mM ATP.