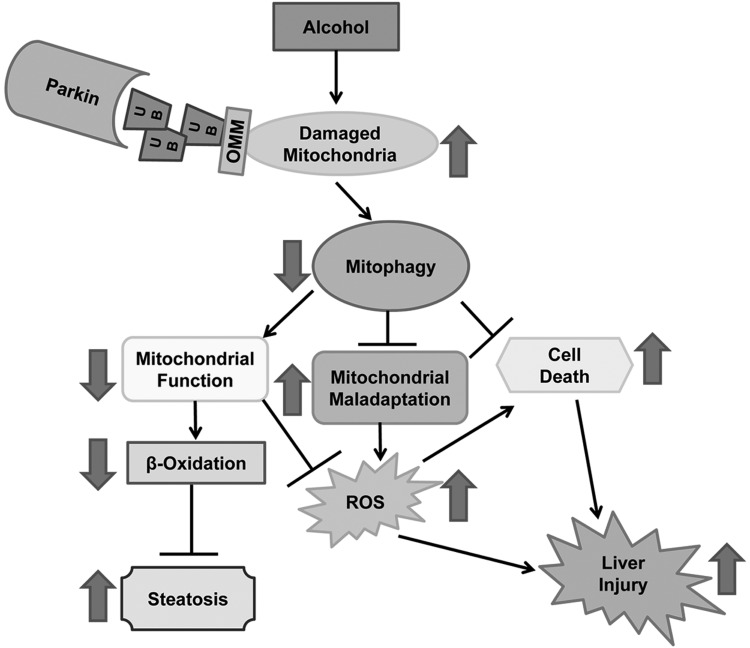
Fig. 9.
Summary of the role of Parkin in alcohol-induced steatosis and liver injury. Parkin is protective against alcohol-induced liver injury, oxidative stress, and steatosis by promoting mitophagy. Decreased mitophagy due to the absence of Parkin may lead to impaired mitochondrial function, decreased β oxidation, increased reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation as well as mitochondrial maladaptation (fewer elongated mitochondria and more swollen mitochondria), resulting in increased steatosis, cell death, and liver injury after alcohol treatment. Consequences of Parkin loss after alcohol treatment are shown by large arrows. ROS, reactive oxygen species; UB, ubiquitin; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane protein.